Hexokinase 2 Is an Intracellular Glucose Sensor of Yeast Cells That Maintains the Structure and Activity of Mig1 Protein Repressor Complex
- PMID: 26865637
- PMCID: PMC4817161
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.711408
Hexokinase 2 Is an Intracellular Glucose Sensor of Yeast Cells That Maintains the Structure and Activity of Mig1 Protein Repressor Complex
Abstract
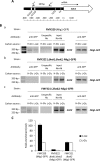
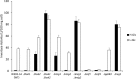
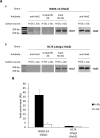
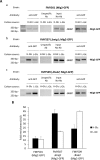
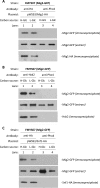
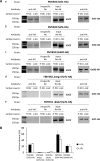
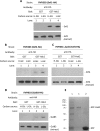
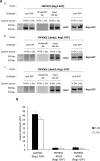
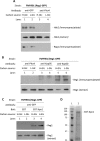
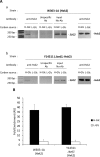
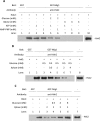
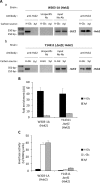
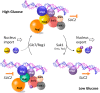
Hexokinase 2 (Hxk2) fromSaccharomyces cerevisiaeis a bi-functional enzyme, being both a catalyst in the cytosol and an important regulator of the glucose repression signal in the nucleus. Despite considerable recent progress, little is known about the regulatory mechanism that controls nuclear Hxk2 association with theSUC2promoter chromatin and how this association is necessary forSUC2gene repression. Our data indicate that in theSUC2promoter context, Hxk2 functions through a variety of structurally unrelated factors, mainly the DNA-binding Mig1 and Mig2 repressors and the regulatory Snf1 and Reg1 factors. Hxk2 sustains the repressor complex architecture maintaining transcriptional repression at theSUC2gene. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation assays, we discovered that the Hxk2 in its open configuration, at low glucose conditions, leaves the repressor complex that induces its dissociation and promotesSUC2gene expression. In high glucose conditions, Hxk2 adopts a close conformation that promotes Hxk2 binding to the Mig1 protein and the reassembly of theSUC2repressor complex. Additional findings highlight the possibility that Hxk2 constitutes an intracellular glucose sensor that operates by changing its conformation in response to cytoplasmic glucose levels that regulate its interaction with Mig1 and thus its recruitment to the repressor complex of theSUC2promoter. Thus, our data indicate that Hxk2 is more intimately involved in gene regulation than previously thought.
Keywords: Saccharomyces cerevisiae; gene expression; glucose; glucose signaling; hexokinase; repressor protein.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Comment in
-
Regulatory Function of Hexokinase 2 in Glucose Signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2016 Aug 5;291(32):16477. doi: 10.1074/jbc.L116.735514. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27496957 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Nuclear Hexokinase 2 Acts as a Glucose Sensor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2016 Aug 5;291(32):16478. doi: 10.1074/jbc.L116.738237. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27496958 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Struhl K. (1995) Yeast transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Genet. 29, 651–674 - PubMed
-
- Malavé T. M., and Dent S. Y. (2006) Transcriptional repression by Tup1-Ssn6. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 84, 437–443 - PubMed
-
- Redd M. J., Arnaud M. B., and Johnson A. D. (1997) A complex composed of tup1 and ssn6 represses transcription in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 11193–11197 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

