Therapeutic potential of Polyalthia cerasoides stem bark extracts against oxidative stress and nociception
- PMID: 26865738
- PMCID: PMC4728867
- DOI: 10.4103/0257-7941.171667
Therapeutic potential of Polyalthia cerasoides stem bark extracts against oxidative stress and nociception
Abstract
Background: Polyalthia cerasoides is a medicinal plant known for its ethnopharmacological importance. Despite this, investigation related to its therapeutic benefit is still unexplored.
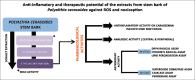
Aim: To evaluate the stem bark extracts of Polyalthia cerasoides for pharmacological activities relating to inflammation, nociception and oxidative stress using in vivo and in vitro models.
Materials and methods: Pet ether, ethyl acetate and chloroform fractions of the stem bark were evaluated for anti-inflammatory activity by carrageenan-induced hind paw edema in rats. Anti-nociceptive activity in mice was assessed using thermally and chemically induced analgesic models. The free radical quenching potential of the extracts was initially analyzed using the in vitro DPPH photometric assay, Hydroxyl radical scavenging and Lipid Peroxidation assays. Then modulatory effect of the extracts on in vivo antioxidant system was evaluated by carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity and subsequent measurements of antioxidant enzymes such as Superoxide dismutase, Catalase and Peroxidase from the liver homogenate.
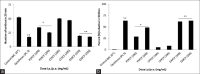
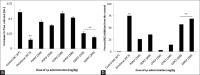
Results: Among the tested fractions, ethyl acetate extract had substantially inhibited the inflammation by 68.5% that was induced by subcutaneous carrageenan injection whereas pet ether and chloroform extract showed only minimal inhibitory effect. Investigation of the anti-nociceptive activity revealed that the ethyl acetate fractions had significantly repressed the algesia in both the analgesic experimental models. In vitro and in vivo individual antioxidant assays demonstrated that the ethyl acetate fraction has strong free radical quenching potential which also restores the endogenous hepatic enzymes.
Conclusion: The ethyl acetate fraction enriched with flavinoids and steroids from Polyalthia cerasoides stem bark has potent bioactivity to combat inflammation, ROS and pain. This needs further characterization for potential therapeutic applications.
Keywords: Analgesia; anti-inflamatory; carageenan; catalase; lipid peroxidation; nociception; reactive oxygen species.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antiproliferative, apoptotic, and antimutagenic properties of stem bark and seed fractions of Polyalthia cerasoides (Roxb.).J Cancer Res Ther. 2021 Oct-Dec;17(6):1339-1346. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_1170_19. J Cancer Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34916363
-
Pharmacological Potential of Tetrahydrofurano/Pyrano Quinoline and Benzo[b]furoindolyl Derivatives in Acute Inflammation, Pain and Oxidative Stress.Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2015;13(3):165-73. doi: 10.2174/1871523014666141217125732. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25515170
-
Investigations on anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of Alnus nitida Spach (Endl). stem bark in Sprague Dawley rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Feb 23;198:407-416. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.01.041. Epub 2017 Jan 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28119101
-
Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity of Mimosa acutistipula (Mart.) Benth.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Mar 1;303:115964. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115964. Epub 2022 Nov 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36436717
-
Isolation and characterization of anti-inflammatory and analgesic compounds from Uapaca staudtii Pax (Phyllanthaceae) stem bark.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 6;269:113737. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113737. Epub 2021 Jan 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33359855
Cited by
-
Phytochemical Screening on Phenolic, Flavonoid Contents, and Antioxidant Activities of Six Indigenous Plants Used in Traditional Thai Medicine.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 30;24(17):13425. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713425. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686230 Free PMC article.
-
Defensive Mechanisms in Cucurbits against Melon Fly (Bactrocera cucurbitae) Infestation through Excessive Production of Defensive Enzymes and Antioxidants.Molecules. 2021 Oct 20;26(21):6345. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216345. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34770754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goudarshivananavar BC, Vigneshwaran V, Dharmappa KK, Pramod SN. Pharmacological potential of tetrahydrofurano/pyrano quinoline and benzo[b] furoindolyl derivatives in acute inflammation, pain and oxidative stress. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2015;13:165–73. - PubMed
-
- Govindarajan R, Vijayakumar M, Pushpangadan P. Antioxidant approach to disease management and the role of ‘Rasayana’ herbs of Ayurveda. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;99:165–78. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

