Impact of 10-weeks of yoga practice on flexibility and balance of college athletes
- PMID: 26865768
- PMCID: PMC4728955
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-6131.171710
Impact of 10-weeks of yoga practice on flexibility and balance of college athletes
Abstract
Background: With clearer evidence of its benefits, coaches, and athletes may better see that yoga has a role in optimizing performance.
Aims: To determine the impact of yoga on male college athletes (N = 26).
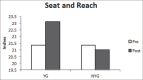
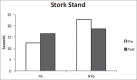
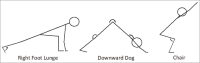
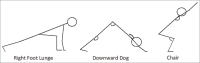
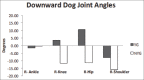
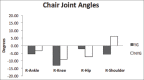
Methods: Over a 10-week period, a yoga group (YG) of athletes (n = 14) took part in biweekly yoga sessions; while a nonyoga group (NYG) of athletes (n = 12) took part in no additional yoga activity. Performance measures were obtained immediately before and after this period. Measurements of flexibility and balance, included: Sit-reach (SR), shoulder flexibility (SF), and stork stand (SS); dynamic measurements consisted of joint angles (JA) measured during the performance of three distinct yoga positions (downward dog [DD]; right foot lunge [RFL]; chair [C]).
Results: Significant gains were observed in the YG for flexibility (SR, P = 0.01; SF, P = 0.03), and balance (SS, P = 0.05). No significant differences were observed in the NYG for flexibility and balance. Significantly, greater JA were observed in the YG for: RFL (dorsiflexion, l-ankle; P = 0.04), DD (extension, r-knee, P = 0.04; r-hip; P = 0.01; flexion, r-shoulder; P = 0.01) and C (flexion, r-knee; P = 0.01). Significant JA differences were observed in the NYG for: DD (flexion, r-knee, P = 0.01: r-hip, P = 0.05; r-shoulder, P = 0.03) and C (flexion r-knee, P = 0.01; extension, r-shoulder; P = 0.05). A between group comparison revealed the significant differences for: RFL (l-ankle; P = 0.01), DD (r-knee, P = 0.01; r-hip; P = 0.01), and C (r-shoulder, P = 0.02).
Conclusions: Results suggest that a regular yoga practice may increase the flexibility and balance as well as whole body measures of male college athletes and therefore, may enhance athletic performances that require these characteristics.
Keywords: Athletes; performance; training.
Figures



References
-
- Ross A, Thomas S. The health benefits of yoga and exercise: A review of comparison studies. J Altern Complement Med. 2010;16:3–12. - PubMed
-
- Pal A, Srivastava N, Tiwari S, Verma NS, Narain VS, Agrawal GG, et al. Effect of yogic practices on lipid profile and body fat composition in patients of coronary artery disease. Complement Ther Med. 2011;19:122–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
