Managing Complications of Fillers: Rare and Not-So-Rare
- PMID: 26865784
- PMCID: PMC4728901
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-2077.172191
Managing Complications of Fillers: Rare and Not-So-Rare
Abstract
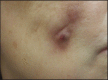
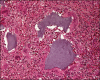
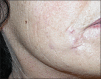
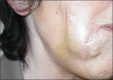
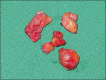
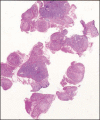
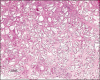
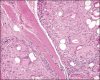
Fillers belong to the most frequently used beautifying products. They are generally well tolerated, but any one of them may occasionally produce adverse side effects. Adverse effects usually last as long as the filler is in the skin, which means that short-lived fillers have short-term side effects and permanent fillers may induce life-long adverse effects. The main goal is to prevent them, however, this is not always possible. Utmost care has to be given to the prevention of infections and the injection technique has to be perfect. Treatment of adverse effects is often with hyaluronidase or steroid injections and in some cases together with 5-fluorouracil plus allopurinol orally. Histological examination of biopsy specimens often helps to identify the responsible filler allowing a specific treatment to be adapted.
Keywords: Complications; blindness; fillers; hyaluronic acid.
Figures





References
-
- Fulton J, Caperton C, Weinkle S, Dewandre L. Filler injections with the blunt-tip microcannula. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:1098–103. - PubMed
-
- Lazzeri D, Agostini T, Figus M, Nardi M, Pantaloni M, Lazzeri S. Blindness following cosmetic injections of the face. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;129:995–1012. - PubMed
-
- Park SW, Woo SJ, Park KH, Huh JW, Jung C, Kwon OK. Iatrogenic retinal artery occlusion caused by cosmetic facial filler injections. Am J Ophthalmol. 2012;154:653–62.e1. - PubMed
-
- Beleznay K, Carruthers JDA, Humphrey S, Jones D. Avoiding an treating blindness from fillers: a review oif the world literature. Dermatol surg. 2015;41:1097–117. - PubMed
-
- Glaich AS, Cohen JL, Goldberg LH. Injection necrosis of the glabella: Protocol for prevention and treatment after use of dermal fillers. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:276–81. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

