Treatment of Postinflammatory Pigmentation Due to Acne with Q-Switched Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet In 78 Indian Cases
- PMID: 26865787
- PMCID: PMC4728904
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-2077.172196
Treatment of Postinflammatory Pigmentation Due to Acne with Q-Switched Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet In 78 Indian Cases
Abstract
Background: Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is a common sequela seen in the Indian population following affliction by acne. It is psychologically extremely disturbing for the patients and can severely affect the quality of life. Very few therapeutic modalities have proved to be really efficacious in this condition.
Aims: The aim was to review our experience with 1,064-nm Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (QSNY) laser in the treatment of PIH.
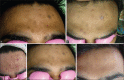
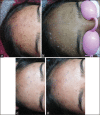
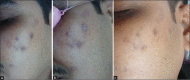
Materials and methods: Seventy-eight patients with postacne hyperpigmentation were included in the study. They were treated with six sessions at two weekly intervals using a 1,064-nm QSNY laser. Patient and physician scores were assessed at 1 month and 3 months after the last treatment. Clinical photographs also were reviewed to determine the efficacy. Adverse effects were noted.
Results: Seventy percent of the patients reported significant improvement in hyperpigmentation as compared to the baseline. The majority of the adverse events were limited to mild, brief erythema.
Conclusion: The 1,064-nm QSNY laser is an effective modality for the treatment of PIH caused by acne.
Keywords: Acne; Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (QSNY) laser; hyperpigmentation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment of facial postinflammatory hyperpigmentation with facial acne in Asian patients using a Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser.Dermatol Surg. 2010 Sep;36(9):1374-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4725.2010.01643.x. Epub 2010 Jul 9. Dermatol Surg. 2010. PMID: 20629693
-
A single-blinded, randomized, controlled trial comparing efficacy between low-fluence alexandrite 755-nm picosecond laser and low-fluence neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) 1064-nm picosecond laser for the treatment of ultraviolet B-induced hyperpigmentation.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022 Mar;21(3):1036-1044. doi: 10.1111/jocd.14591. Epub 2021 Nov 13. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 34773725 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of an epidermal growth factor-containing cream on postinflammatory hyperpigmentation after 1064-nm Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser treatment of acquired bilateral nevus of Ota-like macules (Hori's nevus) in Asians: A split-face, double-blinded, randomized controlled study.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022 May;21(5):2031-2037. doi: 10.1111/jocd.14765. Epub 2022 Jan 23. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35066982 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of erbium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet fractional resurfacing laser for treatment of facial acne scars.Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013 Mar-Apr;79(2):193-8. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.107635. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013. PMID: 23442457 Review.
-
The evolution of melasma therapy: targeting melanosomes using low-fluence Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet lasers.Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2012 Jun;31(2):126-32. doi: 10.1016/j.sder.2012.02.002. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2012. PMID: 22640433 Review.
Cited by
-
Review of Laser Treatments for Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation in Skin of Color.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023 May;24(3):381-396. doi: 10.1007/s40257-023-00759-7. Epub 2023 Feb 13. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 36781686 Review.
-
Low-Fluence Q-Switch 1064 Nm Laser Combined With Oral Tranexamic Acid: A Quicker Treatment for Laser-Induced Postinflammatory Hyperpigmentation.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Feb;24(2):e70018. doi: 10.1111/jocd.70018. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39927593 Free PMC article.
-
Lasers for the treatment of erythema, dyspigmentation, and decreased elasticity in macular acne scars: a systematic review.Lasers Med Sci. 2022 Dec;37(9):3321-3331. doi: 10.1007/s10103-022-03621-0. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Lasers Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35918567
-
Evaluation of Efficacy and Safety of Low-Fluence Q-Switched 1064-nm Laser in Infra-orbital Hyperpigmentation Based on Biometric Parameters.J Lasers Med Sci. 2022 Apr 12;13:e16. doi: 10.34172/jlms.2022.16. eCollection 2022. J Lasers Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35996487 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation in Skin of Colour: A Systematic Review.J Cutan Med Surg. 2024 Sep-Oct;28(5):473-480. doi: 10.1177/12034754241265716. Epub 2024 Jul 29. J Cutan Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39075672 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: A comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387–94. - PubMed
-
- Lacz NL, Vafaie J, Kihiczak NI, Schwartz RA. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: A common but troubling condition. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:362–5. - PubMed
-
- Taylor SC, Cook-Bolden F, Rahman Z, Strachan D. Acne vulgaris in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(Suppl 2):S98–106. - PubMed
-
- Grimes PE. Managment of hyperpigmentation in darker racial ethnic groups. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009;28:77–85. - PubMed
-
- Taylor CR, Anderson RR. Ineffective treatment of refractory melasma and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation by Q-switched ruby laser. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1994;20:592–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

