Customized Orbital Decompression Surgery Combined with Eyelid Surgery or Strabismus Surgery in Mild to Moderate Thyroid-associated Ophthalmopathy
- PMID: 26865797
- PMCID: PMC4742639
- DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2016.30.1.1
Customized Orbital Decompression Surgery Combined with Eyelid Surgery or Strabismus Surgery in Mild to Moderate Thyroid-associated Ophthalmopathy
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of customized orbital decompression surgery combined with eyelid surgery or strabismus surgery for mild to moderate thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (TAO).
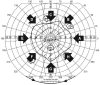
Methods: Twenty-seven consecutive subjects who were treated surgically for proptosis with disfigurement or diplopia after medical therapy from September 2009 to July 2012 were included in the analysis. Customized orbital decompression surgery with correction of eyelid retraction and extraocular movement disorders was simultaneously performed. The patients had a minimum preoperative period of 3 months of stable range of ocular motility and eyelid position. All patients had inactive TAO and were euthyroid at the time of operation. Preoperative and postoperative examinations, including vision, margin reflex distance, Hertel exophthalmometry, ocular motility, visual fields, Goldmann perimetry, and subject assessment of the procedure, were performed in all patients. Data were analyzed using paired t-test (PASW Statistics ver. 18.0).
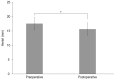
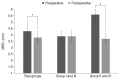
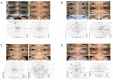
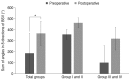
Results: Forty-nine decompressions were performed on 27 subjects (16 females, 11 males; mean age, 36.6 ± 11.6 years). Twenty-two patients underwent bilateral operations; five required only unilateral orbital decompression. An average proptosis of 15.6 ± 2.2 mm (p = 0.00) was achieved, with a mean preoperative Hertel measurement of 17.6 ± 2.2 mm. Ocular motility was corrected through recession of the extraocular muscle in three cases, and no new-onset diplopia or aggravated diplopia was noted. The binocular single vision field increased in all patients. Eyelid retraction correction surgery was simultaneously performed in the same surgical session in 10 of 49 cases, and strabismus and eyelid retraction surgery were performed in the same surgical session in two cases. Margin reflex distance decreased from a preoperative average of 4.3 ± 0.8 to 3.8 ± 0.5 mm postoperatively.
Conclusions: The customized orbital decompression procedure decreased proptosis and improved diplopia, in a range comparable to those achieved through more stepwise techniques, and had favorable cosmetic results when combined with eyelid surgery or strabismus surgery for mild to moderate TAO.
Keywords: Diplopia; Exophthalmos; Eyelid retraction; Graves ophthalmopathy; Orbital decompression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Simultaneous orbital decompression and correction of upper eyelid retraction versus staged procedures in thyroid-related orbitopathy.Ophthalmology. 2005 May;112(5):923-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2004.12.028. Ophthalmology. 2005. PMID: 15878077
-
Postoperative Changes in Strabismus, Ductions, Exophthalmometry, and Eyelid Retraction After Orbital Decompression for Thyroid Orbitopathy.Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017 Jul/Aug;33(4):289-293. doi: 10.1097/IOP.0000000000000758. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017. PMID: 27487726
-
Follow-up of transnasal orbital decompression in severe Graves' ophthalmopathy.Ophthalmology. 2001 Feb;108(2):400-4. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(00)00533-9. Ophthalmology. 2001. PMID: 11158820
-
Efficacy and side effects of 'swinging eyelid' orbital decompression in Graves' orbitopathy: a proposal for standardized evaluation of diplopia.Eye (Lond). 2006 Feb;20(2):154-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.eye.6701827. Eye (Lond). 2006. PMID: 15746952 Review.
-
Influence of orbital decompression on upper eyelid retraction in Graves' orbitopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Orbit. 2024 Aug;43(4):549-554. doi: 10.1080/01676830.2023.2248621. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Orbit. 2024. PMID: 37611061
Cited by
-
The Challenges and Therapeutic Prospects in Eye Disease.J Pers Med. 2023 May 31;13(6):930. doi: 10.3390/jpm13060930. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37373919 Free PMC article.
-
Future Projections in Thyroid Eye Disease.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Aug 8;107(Suppl_1):S47-S56. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac252. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 36346684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors Predicting the Success of Combined Orbital Decompression and Strabismus Surgery in Thyroid-Associated Orbitopathy.J Pers Med. 2022 Jan 31;12(2):186. doi: 10.3390/jpm12020186. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35207674 Free PMC article.
-
Position and size of the sphenoid door jamb in the lateral orbital wall for the orbital decompression.Anat Cell Biol. 2019 Sep;52(3):242-249. doi: 10.5115/acb.19.101. Epub 2019 Sep 26. Anat Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31598352 Free PMC article.
-
[Orbital decompression : Indications, technique, results].HNO. 2017 Dec;65(12):1023-1038. doi: 10.1007/s00106-017-0429-6. HNO. 2017. PMID: 29085976 German.
References
-
- McCord CD Jr, Tanenbaum M, Nunery WR, editors. Oculoplastic surgery. 3rd ed. New York: Raven Press; 1995. p. 379.
-
- Kazim M, Goldberg RA, Smith TJ. Insights into the pathogenesis of thyroid-associated orbitopathy: evolving rationale for therapy. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120:380–386. - PubMed
-
- Trokel S, Kazim M, Moore S. Orbital fat removal: decompression for Graves orbitopathy. Ophthalmology. 1993;100:674–682. - PubMed
-
- Park JH, Lee TS, Kay KM. Long-term result of fat orbital decompression. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010;51:473–478.
-
- Kamer L, Noser H, Schramm A, et al. Anatomy-based surgical concepts for individualized orbital decompression surgery in graves orbitopathy: I. orbital size and geometry. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;26:348–352. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources