Possible neurocognitive benefits of exercise in persons with heart failure
- PMID: 26865870
- PMCID: PMC4745145
- DOI: 10.1186/s11556-015-0151-x
Possible neurocognitive benefits of exercise in persons with heart failure
Abstract
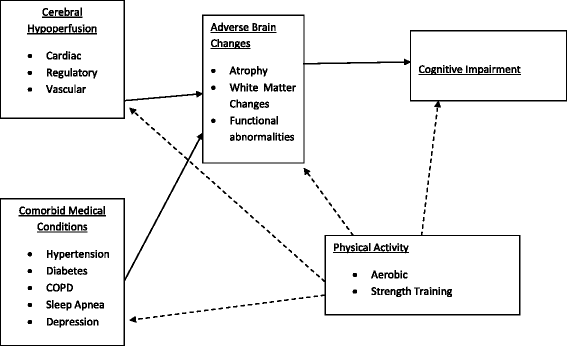
More than 6 million Americans have heart failure (HF) and more than 500,000 are diagnosed each year. In addition to its many adverse medical consequences, HF is also a significant risk factor for neurological disorders like Alzheimer's disease and associated with cognitive impairment long prior to the onset of these conditions. Converging bodies of literature suggest cognitive dysfunction in HF may be at least partially modifiable. One key mechanism for cognitive improvement is improved cerebral blood flow, which may be possible with exercise in patients with HF. This brief review provides a model for the likely neurocognitive benefits of exercise in HF and encourages further work in this area.
Keywords: Exercise; Heart failure; Memory.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neurocognitive Disorders in Heart Failure: Novel Pathophysiological Mechanisms Underpinning Memory Loss and Learning Impairment.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Dec;56(12):8035-8051. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01655-0. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31165973 Review.
-
Atrial fibrillation exacerbates cognitive dysfunction and cerebral perfusion in heart failure.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2015 Feb;38(2):178-86. doi: 10.1111/pace.12543. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25492027 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise and Cognitive Training as a Strategy to Improve Neurocognitive Outcomes in Heart Failure: A Pilot Study.Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2019 Aug;27(8):809-819. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2019.01.211. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30910420 Free PMC article.
-
Heart Failure and Cognitive Impairment in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study.J Gen Intern Med. 2018 Oct;33(10):1721-1728. doi: 10.1007/s11606-018-4556-x. Epub 2018 Jul 20. J Gen Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 30030736 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive decline in heart failure: Biomolecular mechanisms and benefits of exercise.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022 Nov 1;1868(11):166511. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2022.166511. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022. PMID: 35932891 Review.
Cited by
-
Cognition, Physical Function, and Quality of Life in Older Patients With Acute Decompensated Heart Failure.J Card Fail. 2021 Mar;27(3):286-294. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2020.09.007. Epub 2020 Sep 18. J Card Fail. 2021. PMID: 32956816 Free PMC article.
-
Improving cerebral oxygenation, cognition and autonomic nervous system control of a chronic alcohol abuser through a three-month running program.Addict Behav Rep. 2017 Aug 31;6:83-89. doi: 10.1016/j.abrep.2017.08.004. eCollection 2017 Dec. Addict Behav Rep. 2017. PMID: 29450240 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive Deficit in Heart Failure and the Benefits of Aerobic Physical Activity.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2018 Jan;110(1):91-94. doi: 10.5935/abc.20180002. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29538528 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological Aspects of Heart Failure.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2016 Dec;18(12):119. doi: 10.1007/s11886-016-0799-5. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27796856 Review.
-
Atrial fibrillation and cognitive function in patients with heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Heart Fail Rev. 2017 Jan;22(1):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s10741-016-9587-y. Heart Fail Rev. 2017. PMID: 27844178
References
-
- Almeida JRC, Alves TCTF, Wajngarten M, Rays J, Castro CC, Cordeiro Q, Busatto GF. Late-life depression, heart failure, and frontal white matter hyperintensity: a structural magnetic resonance imaging study. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2005;38:431–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous