Electrophoretically prepared hybrid materials for biopolymer hydrogel and layered ceramic nanoparticles
- PMID: 26865985
- PMCID: PMC4748479
- DOI: 10.1186/s40824-016-0048-4
Electrophoretically prepared hybrid materials for biopolymer hydrogel and layered ceramic nanoparticles
Abstract
Background: In order to obtain biomaterials with controllable physicochemical properties, hybrid biomaterials composed of biocompatible biopolymers and ceramic nanoparticles have attracted interests. In this study, we prepared biopolymer/ceramic hybrids consisting of various natural biopolymers and layered double hydroxide (LDH) ceramic nanoparticles via an electrophoretic method. We studied the structures and controlled-release properties of these materials.
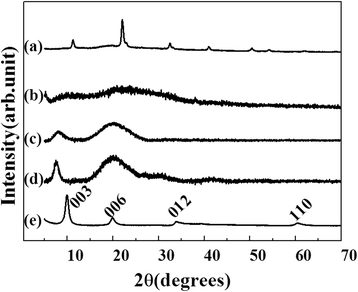
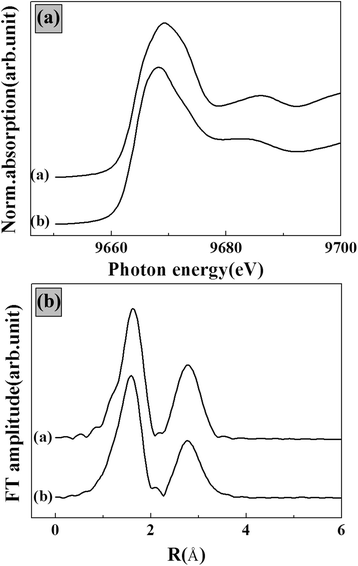
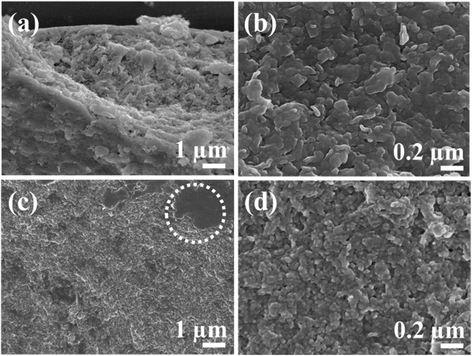
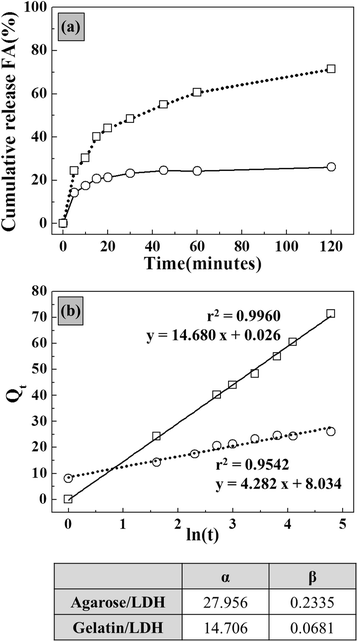
Results and discussion: X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns and X-ray absorption spectra (XAS) showed that LDH nanoparticles were formed in a biopolymer hydrogel through electrophoretic reaction. Scanning electron microscopic (SEM) images showed that the ceramic nanoparticles were homogeneously distributed throughout the hydrogel matrix. An antioxidant agent (i.e., ferulic acid) was loaded onto agarose/LDH and gelatin/LDH hybrids, and the time-dependent release of ferulic acid was investigated via high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for kinetic model fitting.
Conclusions: Biopolymer/LDH hybrid materials that were prepared by electrophoretic method created a homogeneous composite of two components and possessed controllable drug release properties according to the type of biopolymer.
Keywords: Agarose; Biopolymer; Ceramic; Controlled release; Electrophoretic synthesis; Gelatin; Layered double hydroxide.
Figures
References
-
- Tathe A, Ghodke M, Nikalje AP. A brief review: biomaterials and their application. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2010;2:19–23.
-
- Patel NR, Gohil PP. A review on biomaterials: scope, applications & human anatomy significance. Int J Emerging Technol Adv Eng. 2012;2:91–101.
-
- Lee HB. Needs and opportunities for the biomaterials industry. Polym Sci Technol. 1994;5:566–76.
-
- Griffith L. Polymeric biomaterials. Acta Mater. 2000;48:263–77. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(99)00299-2. - DOI
-
- Petzetakis N, Dove AP, O’Reilly RK. Cylindrical micelles from the living crystallization-driven self-assembly of poly (lactide)-containing block copolymers. Chem Sci. 2011;2:955–60. doi: 10.1039/C0SC00596G. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

