Cholinergic mechanisms of the context preexposure facilitation effect in adolescent rats
- PMID: 26866360
- PMCID: PMC4792729
- DOI: 10.1037/bne0000134
Cholinergic mechanisms of the context preexposure facilitation effect in adolescent rats
Abstract
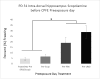
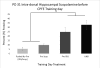
The context preexposure facilitation effect (CPFE) is a variant of contextual fear conditioning in which context learning, context-shock association, and expression of context conditioning occur in 3 separate phases-preexposure, training, and testing. During the preexposure phase, the CPFE is disrupted by hippocampal NMDA receptor blockade in juvenile rats (Schiffino et al., 2011), and a similar deficit is seen with a subcutaneous injection of the muscarinic receptor antagonist, scopolamine, in adult mice (Brown, Kennard, Sherer, Comalli, & Woodruff-Pak, 2011). As a foundation for further developmental research, the present study examined the role of cholinergic function in the CPFE in adolescent rats during each phase of the CPFE protocol. In Experiment 1, an i.p injection of either 0.5 or 1.0 mg/kg dose of scopolamine administered prior to all 3 phases of the CPFE protocol impaired the CPFE. Experiment 2 further showed that a 0.5 mg/kg injection prior to just 1 of the 3 phases of the CPFE also disrupted contextual fear conditioning. We further showed that the CPFE is impaired by localized scopolamine infusions into dorsal hippocampus on the preexposure day (Experiment 3a), training day (Experiment 3b), and test day (Experiment 3c). These findings demonstrate a role of cholinergic signaling in hippocampus during each of the 3 phases of the CPFE in adolescent rats. Implications for the development and neural basis of the CPFE are discussed. (PsycINFO Database Record
(c) 2016 APA, all rights reserved).
Figures




Similar articles
-
Antagonism of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in medial prefrontal cortex disrupts the context preexposure facilitation effect.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2017 Sep;143:27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2017.04.003. Epub 2017 Apr 11. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2017. PMID: 28411153 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA receptor antagonism disrupts acquisition and retention of the context preexposure facilitation effect in adolescent rats.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Mar 15;301:168-77. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.12.025. Epub 2015 Dec 19. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26711910 Free PMC article.
-
Role of dorsal and ventral hippocampal muscarinic receptor activity in acquisition and retention of contextual fear conditioning.Behav Neurosci. 2020 Oct;134(5):460-470. doi: 10.1037/bne0000411. Behav Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33001682
-
The place of the hippocampus in fear conditioning.Eur J Pharmacol. 2003 Feb 28;463(1-3):217-23. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(03)01283-4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12600712 Review.
-
Pre-treatment hippocampal functioning impacts context renewal for cholinergic modulated exposure therapy.Biol Psychol. 2021 Oct;165:108167. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2021.108167. Epub 2021 Oct 5. Biol Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34624624 Review.
Cited by
-
Neonatal ethanol exposure impairs long-term context memory formation and prefrontal immediate early gene expression in adolescent rats.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Feb 1;359:386-395. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.11.018. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30447241 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of the immediate early genes c-Fos, Arc, Egr-1, and Npas4 during long-term memory formation in the context preexposure facilitation effect (CPFE).Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018 Jan;147:128-138. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2017.11.016. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018. PMID: 29222058 Free PMC article.
-
Age and experience dependent changes in Egr-1 expression during the ontogeny of the context preexposure facilitation effect (CPFE).Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018 Apr;150:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2018.02.008. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018. PMID: 29452227 Free PMC article.
-
Differential involvement of the medial prefrontal cortex across variants of contextual fear conditioning.Learn Mem. 2017 Jul 17;24(8):322-330. doi: 10.1101/lm.045286.117. Print 2017 Aug. Learn Mem. 2017. PMID: 28716952 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA receptors and the ontogeny of post-shock and retention freezing during contextual fear conditioning.Dev Psychobiol. 2020 Apr;62(3):380-385. doi: 10.1002/dev.21928. Epub 2019 Oct 17. Dev Psychobiol. 2020. PMID: 31621064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anagnostaras SG, Maren S, Sage JR, Goodrich S, Fanselow MS. Scopolamine and Pavlovian fear conditioning in rats: Dose-effect analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999;21(6):731–744. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(99)00083-4. - PubMed
-
- Anagnostaras SG, Maren S, Fanselow MS. Scopolamine selectively disrupts the acquisition of contextual fear conditioning in rats. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory. 1995;64(3):191–194. Retrieved from http://search.proquest.com/docview/618943504?accountid=10457. - PubMed
-
- Aramakis VB, Bandrowski AE, Ashe JH. Role of muscarinic receptors, G-proteins, and intracellular messengers in muscarinic modulation of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission. Synapse. 1999;32(4):262–75. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Barack J, Dudai Y. Early septal lesion: Effect on the development of the cholinergic system in rat hippocampus. Brain Research. 1980;185(1980):323–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

