Dentists' and Parents' Attitude Toward Nitrous Oxide Use in Kuwait
- PMID: 26866406
- PMCID: PMC4751521
- DOI: 10.2344/14-00008.1
Dentists' and Parents' Attitude Toward Nitrous Oxide Use in Kuwait
Abstract
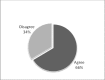
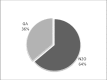
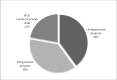
The aim of this study was to investigate the attitude of dentists in Kuwait toward the use of nitrous oxide sedation as a behavior management technique (BMT) for pediatric patients and assess their training in nitrous oxide sedation. In addition, we assessed parents' knowledge of and attitude toward the use of nitrous oxide as a BMT for their children. The objective was to determine if nitrous oxide sedation is being provided and utilized as a means to enhance dental care for pediatric patients. A cross-sectional survey was randomly distributed to both groups of interest: parents accompanying their children to the dentist and licensed dentists in Kuwait. Participants had to meet certain inclusion criteria to be included in the survey and had to complete the entire questionnaire to be part of the analysis. A total of 381 parents completed the questionnaires. The majority of parents responded that they were unaware of nitrous oxide sedation and were not aware of it as a BMT (79%). Two thirds of the parent would accept nitrous oxide sedation if recommended by a dentist treating their children. Two hundred and one dentists completed the survey and met the inclusion criteria. The majority (74.5%) of dentists were willing to use nitrous oxide as a BMT. However, only 6% were utilizing nitrous oxide sedation and providing it to their child patient if indicated. The main reasons for this huge gap are lack of facilities/equipment and lack of training as indicated by the dentists. This study showed that parents are accepting nitrous oxide sedation as a BMT for their children. It also showed the willingness of the dentists to provide such BMT to their patients. The lack of training and lack of equipment are the main barriers to providing such service to the patients. More training courses and more facilities should be provided to eliminate such barriers.
Keywords: Kuwait; Minimal sedation; Nitrous oxide.
Figures
References
-
- American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD) Guideline on Behavior Guidance for the Pediatric Dental Patient. Chicago, Ill: American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD); 2011.
-
- American Dental Association (ADA) Guidelines for the Use of Sedation and General Anesthesia by Dentists. Chicago, Ill: American Dental Association (ADA); 2012.
-
- American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD) Guideline on Use of Nitrous Oxide for Pediatric Dental Patients. Chicago, Ill: American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD); 2013. - PubMed
-
- Hosey MT. UK National Clinical Guidelines in Paediatric Dentistry. Managing anxious children: the use of conscious sedation in paediatric dentistry. Int J Paed Dent. 2002;12:359–372. - PubMed
-
- Council of European Dentists. The Use of Nitrous Oxide Inhalation Sedation in Dentistry. Bruxelles, Belgium: Council of European Dentists; 2012.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous