C60 fullerene localization and membrane interactions in RAW 264.7 immortalized mouse macrophages
- PMID: 26866469
- PMCID: PMC4761875
- DOI: 10.1039/c5nr07003a
C60 fullerene localization and membrane interactions in RAW 264.7 immortalized mouse macrophages
Abstract
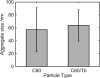
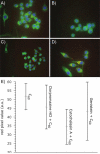
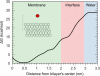
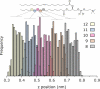
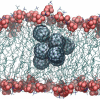
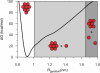
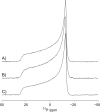
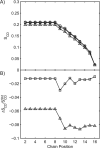
There continues to be a significant increase in the number and complexity of hydrophobic nanomaterials that are engineered for a variety of commercial purposes making human exposure a significant health concern. This study uses a combination of biophysical, biochemical and computational methods to probe potential mechanisms for uptake of C60 nanoparticles into various compartments of living immune cells. Cultures of RAW 264.7 immortalized murine macrophage were used as a canonical model of immune-competent cells that are likely to provide the first line of defense following inhalation. Modes of entry studied were endocytosis/pinocytosis and passive permeation of cellular membranes. The evidence suggests marginal uptake of C60 clusters is achieved through endocytosis/pinocytosis, and that passive diffusion into membranes provides a significant source of biologically-available nanomaterial. Computational modeling of both a single molecule and a small cluster of fullerenes predicts that low concentrations of fullerenes enter the membrane individually and produce limited perturbation; however, at higher concentrations the clusters in the membrane causes deformation of the membrane. These findings are bolstered by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) of model membranes that reveal deformation of the cell membrane upon exposure to high concentrations of fullerenes. The atomistic and NMR models fail to explain escape of the particle out of biological membranes, but are limited to idealized systems that do not completely recapitulate the complexity of cell membranes. The surprising contribution of passive modes of cellular entry provides new avenues for toxicological research that go beyond the pharmacological inhibition of bulk transport systems such as pinocytosis.
Figures

References
-
- Aschberger K, Johnston HJ, Stone V, Aitken RJ, Tran CL, Hankin SM, Peters SAK, Christensen FM. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010;58:455–473. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen GD, Roursgaard M, Jensen KA, Poulsen SS, Larsen ST. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008;103:197–208. - PubMed
-
- Johnston HJ, Hutchison GR, Christensen FM, Aschberger K, Stone V. Toxicol. Sci. 2010;114:162–182. - PubMed
-
- Zakharian TY, Seryshev A, Sitharaman B, Gilbert BE, Knight V, Wilson LJ. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005;127:12508–12509. - PubMed
-
- Montellano A, Ros TD, Bianco A, Prato M. Nanoscale. 2011;3:4035–4041. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

