Using an Insect Mushroom Body Circuit to Encode Route Memory in Complex Natural Environments
- PMID: 26866692
- PMCID: PMC4750948
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004683
Using an Insect Mushroom Body Circuit to Encode Route Memory in Complex Natural Environments
Abstract
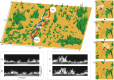
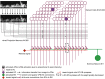
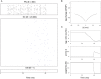
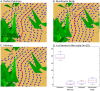
Ants, like many other animals, use visual memory to follow extended routes through complex environments, but it is unknown how their small brains implement this capability. The mushroom body neuropils have been identified as a crucial memory circuit in the insect brain, but their function has mostly been explored for simple olfactory association tasks. We show that a spiking neural model of this circuit originally developed to describe fruitfly (Drosophila melanogaster) olfactory association, can also account for the ability of desert ants (Cataglyphis velox) to rapidly learn visual routes through complex natural environments. We further demonstrate that abstracting the key computational principles of this circuit, which include one-shot learning of sparse codes, enables the theoretical storage capacity of the ant mushroom body to be estimated at hundreds of independent images.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Wehner R. The architecture of the desert ant’s navigational toolkit (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecological News. 2009;12:85–96.
-
- Collett TS, Graham P, Harris RA. Novel landmark-guided routes in ants. J. Exp. Biol. 2007;210:2025–32. - PubMed
-
- Wehner R. Desert ant navigation: How miniature brains solve complex tasks. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sensory, Neural, Behav. Physiol. 2003;189:579–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

