Ovarian Function, Not Age, Predicts the Benefit from Ovarian Suppression or Ablation for Premenopausal Women with Breast Cancer
- PMID: 26866810
- PMCID: PMC4750981
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148849
Ovarian Function, Not Age, Predicts the Benefit from Ovarian Suppression or Ablation for Premenopausal Women with Breast Cancer
Abstract
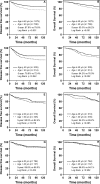
The role of adjuvant ovarian suppression or ablation (OS/OA) in premenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer remains controversial. The purpose of our study was to examine which patients might benefit from the addition of OS/OA to tamoxifen. We analyzed the data of 2065 premenopausal patients with hormone receptor-positive invasive ductal carcinomas who were treated at Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center from 2000 to 2008. The five-year disease-free survival rate (DFSR) and overall survival rate (OSR) were compared by menstrual status and treatment. Compared with patients older than forty years of age, patients younger than forty years old had significant lower DFSRs and OSRs. The addition of OS/OA to tamoxifen increased the DFSR and OSR of patients with normal menstrual cycles after chemotherapy, regardless of their age at diagnosis. Patients with normal menstrual cycles after chemotherapy are the main beneficiaries of an adjuvant OS/OA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ovarian ablation for premenopausal breast cancer: A review of treatment considerations and the impact of premature menopause.Cancer Treat Rev. 2017 Apr;55:26-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.02.005. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017. PMID: 28288389 Review.
-
Combined ovarian ablation and aromatase inhibition as first-line therapy for hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer in premenopausal women: report of three cases.Anticancer Drugs. 2006 Sep;17(8):999-1002. doi: 10.1097/01.cad.0000224456.28898.37. Anticancer Drugs. 2006. PMID: 16940812
-
What is the role of ovarian ablation in the management of primary and metastatic breast cancer today?Oncologist. 2004;9(5):507-17. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.9-5-507. Oncologist. 2004. PMID: 15477635 Review.
-
Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonists in premenopausal hormone receptor-positive breast cancer.Clin Breast Cancer. 2007 Feb;7(6):455-64. doi: 10.3816/CBC.2007.n.002. Clin Breast Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17386122 Review.
-
Adjuvant endocrine therapy for premenopausal women with early breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2007;9(6):115. doi: 10.1186/bcr1830. Breast Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 18190722 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical significance of serum estradiol monitoring in women receiving adjuvant aromatase inhibitor for hormone receptor-positive early breast cancer.Breast. 2024 Dec;78:103818. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2024.103818. Epub 2024 Sep 29. Breast. 2024. PMID: 39357125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davies C, Godwin J, Gray R, Clarke M, Cutter D, Darby S, et al. Relevance of breast cancer hormone receptors and other factors to the efficacy of adjuvant tamoxifen: patient-level meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet. 2011. August 27;378(9793):771–84. 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60993-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aebi S, Gelber S, Castiglione-Gertsch M, Gelber RD, Collins J, Thurlimann B, et al. Is chemotherapy alone adequate for young women with oestrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer? Lancet. 2000. May 27;355(9218):1869–74. - PubMed
-
- Ahn SH, Son BH, Kim SW, Kim SI, Jeong J, Ko SS, et al. Poor outcome of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer at very young age is due to tamoxifen resistance: nationwide survival data in Korea—a report from the Korean Breast Cancer Society. J Clin Oncol. 2007. June 10;25(17):2360–8. - PubMed
-
- Ovarian ablation in early breast cancer: overview of the randomised trials. Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group. Lancet. 1996. November 2;348(9036):1189–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

