Estrogen, SNP-Dependent Chemokine Expression and Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator Regulation
- PMID: 26866883
- PMCID: PMC4771694
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2015-1267
Estrogen, SNP-Dependent Chemokine Expression and Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator Regulation
Abstract
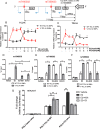
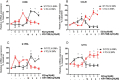
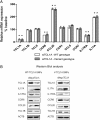
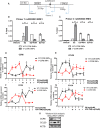
We previously reported, on the basis of a genome-wide association study for aromatase inhibitor-induced musculoskeletal symptoms, that single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) near the T-cell leukemia/lymphoma 1A (TCL1A) gene were associated with aromatase inhibitor-induced musculoskeletal pain and with estradiol (E2)-induced TCL1A expression. Furthermore, variation in TCL1A expression influenced the downstream expression of proinflammatory cytokines and cytokine receptors. Specifically, the top hit genome-wide association study SNP, rs11849538, created a functional estrogen response element (ERE) that displayed estrogen receptor (ER) binding and increased E2 induction of TCL1A expression only for the variant SNP genotype. In the present study, we pursued mechanisms underlying the E2-SNP-dependent regulation of TCL1A expression and, in parallel, our subsequent observations that SNPs at a distance from EREs can regulate ERα binding and that ER antagonists can reverse phenotypes associated with those SNPs. Specifically, we performed a series of functional genomic studies using a large panel of lymphoblastoid cell lines with dense genomic data that demonstrated that TCL1A SNPs at a distance from EREs can modulate ERα binding and expression of TCL1A as well as the expression of downstream immune mediators. Furthermore, 4-hydroxytamoxifen or fulvestrant could reverse these SNP-genotype effects. Similar results were found for SNPs in the IL17A cytokine and CCR6 chemokine receptor genes. These observations greatly expand our previous results and support the existence of a novel molecular mechanism that contributes to the complex interplay between estrogens and immune systems. They also raise the possibility of the pharmacological manipulation of the expression of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in a SNP genotype-dependent fashion.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Aromatase inhibitors, estrogens and musculoskeletal pain: estrogen-dependent T-cell leukemia 1A (TCL1A) gene-mediated regulation of cytokine expression.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Mar 9;14(2):R41. doi: 10.1186/bcr3137. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22405131 Free PMC article.
-
TCL1A Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Estrogen-Mediated Toll-Like Receptor-MYD88-Dependent Nuclear Factor-κB Activation: Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism- and Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator-Dependent Modification of Inflammation and Immune Response.Mol Pharmacol. 2017 Aug;92(2):175-184. doi: 10.1124/mol.117.108340. Epub 2017 Jun 14. Mol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28615284 Free PMC article.
-
TCL1A, a Novel Transcription Factor and a Coregulator of Nuclear Factor κB p65: Single Nucleotide Polymorphism and Estrogen Dependence.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018 Jun;365(3):700-710. doi: 10.1124/jpet.118.247718. Epub 2018 Mar 28. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018. PMID: 29592948 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of estrogen action: selective ligands and receptor pharmacology.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2000 Nov 30;74(5):279-85. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(00)00104-7. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 11162936 Review.
-
The Modes of Dysregulation of the Proto-Oncogene T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma 1A.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 29;13(21):5455. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215455. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771618 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma TNFSF10 levels associated with acamprosate treatment response in patients with alcohol use disorder.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 1;13:986238. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.986238. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36120372 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory SNPs and their widespread effects on the transcriptome.J Biosci. 2018 Dec;43(5):1069-1075. J Biosci. 2018. PMID: 30541964 Review.
-
Genetic predictors to acupuncture response for hot flashes: an exploratory study of breast cancer survivors.Menopause. 2020 Aug;27(8):913-917. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001545. Menopause. 2020. PMID: 32217888 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Calmodulin-like protein 3 is an estrogen receptor alpha coregulator for gene expression and drug response in a SNP, estrogen, and SERM-dependent fashion.Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Aug 18;19(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13058-017-0890-x. Breast Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28821270 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen regulates sex-specific localization of regulatory T cells in adipose tissue of obese female mice.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 2;15(4):e0230885. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230885. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32240221 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

