Heme oxygenase 1 controls early innate immune response of macrophages to Salmonella Typhimurium infection
- PMID: 26866925
- PMCID: PMC6557132
- DOI: 10.1111/cmi.12578
Heme oxygenase 1 controls early innate immune response of macrophages to Salmonella Typhimurium infection
Abstract
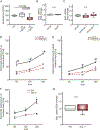
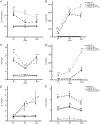
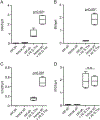
Macrophages are central for the immune control of intracellular microbes. Heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1, hmox) is the first and rate limiting enzyme in the breakdown of heme originating from degraded senescent erythrocytes and heme-proteins, yielding equal amounts of iron, carbon monoxide and biliverdin. HO-1 is strongly up-regulated in macrophages in response to inflammatory signals, including bacterial endotoxin. In view of the essential role of iron for the growth and proliferation of intracellular bacteria along with known effects of the metal on innate immune function, we examined whether HO-1 plays a role in the control of infection with the intracellular bacterium Salmonella Typhimurium. We studied the course of infection in stably-transfected murine macrophages (RAW264.7) bearing a tetracycline-inducible plasmid producing hmox shRNA and in primary HO-1 knockout macrophages. While uptake of bacteria into macrophages was not affected, a significantly reduced survival of intracellular Salmonella was observed upon hmox knockdown or pharmacological hmox inhibition, which was independent of Nramp1 functionality. This could be traced to limitation of iron availability for intramacrophage bacteria along with enhanced stimulation of innate immune effector pathways, including the formation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and increased TNF-α expression. Mechanistically, these latter effects result from intracellular iron limitation with subsequent activation of NF-κB and further inos, tnfa and p47phox transcription along with reduced formation of the anti-inflammatory and radical scavenging molecules, CO and biliverdin as a consequence of HO-1 silencing. Taken together our data provide novel evidence that the infection-driven induction of HO-1 exerts detrimental effects in the early control of Salmonella infection, whereas hmox inhibition can favourably modulate anti-bacterial immune effector pathways of macrophages and promote bacterial elimination.
© 2016 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



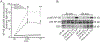
Similar articles
-
The co-ordinated regulation of iron homeostasis in murine macrophages limits the availability of iron for intracellular Salmonella typhimurium.Cell Microbiol. 2007 Sep;9(9):2126-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.00942.x. Epub 2007 Apr 25. Cell Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17466014
-
Slc11a1 (Nramp1) impairs growth of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium in macrophages via stimulation of lipocalin-2 expression.J Leukoc Biol. 2012 Aug;92(2):353-9. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1111554. Epub 2012 Jun 15. J Leukoc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22706314 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoprotective function of heme oxygenase 1 induced by a nitrated cyclic nucleotide formed during murine salmonellosis.J Immunol. 2009 Mar 15;182(6):3746-56. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803363. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19265153
-
[New paradigm of host defense against intracellular pathogens by nitric oxide].Nihon Hansenbyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2009 Feb;78(1):41-7. doi: 10.5025/hansen.78.41. Nihon Hansenbyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2009. PMID: 19227148 Review. Japanese.
-
Heme oxygenase 1 in erythropoiesis: an important regulator beyond catalyzing heme catabolism.Ann Hematol. 2023 Jun;102(6):1323-1332. doi: 10.1007/s00277-023-05193-7. Epub 2023 Apr 12. Ann Hematol. 2023. PMID: 37046065 Review.
Cited by
-
The pathogenicity and virulence of Leishmania - interplay of virulence factors with host defenses.Virulence. 2022 Dec;13(1):903-935. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2074130. Virulence. 2022. PMID: 35531875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Limited Heme Oxygenase Contribution to Modulating the Severity of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium Infection.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 May 24;11(6):1040. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061040. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35739937 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase-4 and -5 Biology in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 31;13:919567. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.919567. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35712726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimycobacterial effect of IFNG (interferon gamma)-induced autophagy depends on HMOX1 (heme oxygenase 1)-mediated increase in intracellular calcium levels and modulation of PPP3/calcineurin-TFEB (transcription factor EB) axis.Autophagy. 2018;14(6):972-991. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1436936. Epub 2018 May 10. Autophagy. 2018. PMID: 29457983 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Biofilms Inhibit the Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Mar 20;7:86. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00086. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28373968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ables GP, Takamatsu D, Noma H, El-Shazly S, Jin HK, Taniguchi T, et al. (2001) The roles of Nramp1 and Tnfa genes in nitric oxide production and their effect on the growth of Salmonella typhimurium in macrophages from Nramp1 congenic and tumor necrosis factor-alpha−/− mice. J Interferon cytokine Res: Off J Int Soc Interferon Cytokine Res 21: 53–62. - PubMed
-
- Armitage AE, Eddowes LA, Gileadi U, Cole S, Spottiswoode N, Selvakumar TA, et al. (2011) Hepcidin regulation by innate immune and infectious stimuli. Blood 118: 4129–4139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

