Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Some Novel Pyrrolizine Derivatives as COX Inhibitors with Anti-Inflammatory/Analgesic Activities and Low Ulcerogenic Liability
- PMID: 26867188
- PMCID: PMC6273963
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21020201
Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Some Novel Pyrrolizine Derivatives as COX Inhibitors with Anti-Inflammatory/Analgesic Activities and Low Ulcerogenic Liability
Abstract
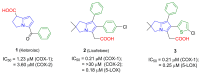
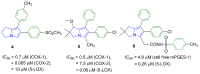
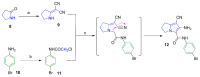
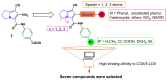
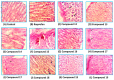
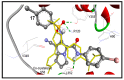
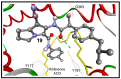
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the most commonly prescribed anti-inflammatory and pain relief medications. However, their use is associated with many drawbacks, including mainly serious gastric and renal complications. In an attempt to circumvent these risks, a set of N-(4-bromophenyl)-7-cyano-6-substituted-H-pyrrolizine-5-carboxamide derivatives were designed, synthesized and evaluated as dual COX/5-LOX inhibitors. The structural elucidation, in vivo anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities using a carrageenan-induced rat paw edema model and hot plate assay, were performed, respectively. From the results obtained, it was found that the newly synthesized pyrrolizines exhibited IC50 values in the range of 2.45-5.69 µM and 0.85-3.44 µM for COX-1 and COX-2, respectively. Interestingly, compounds 12, 13, 16 and 17 showed higher anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities compared to ibuprofen. Among these derivatives, compounds 16 and 19 displayed better safety profile than ibuprofen in acute ulcerogenicity and histopathological studies. Furthermore, the docking studies revealed that compound 17 fits nicely into COX-1 and COX-2 binding sites with the highest binding affinity, while compound 16 exerted the highest binding affinity for 5-LOX. In light of these findings, these novel pyrrolizine-5-carboxamide derivatives represent a promising scaffold for further development into potential dual COX/5-LOX inhibitors with safer gastric profile.
Keywords: 5-LOX; COX; analgesic; anti-inflammatory; pyrrolizine; ulcerogenicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Synthesis, biological evaluation, docking study and ulcerogenicity profiling of some novel quinoline-2-carboxamides as dual COXs/LOX inhibitors endowed with anti-inflammatory activity.Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Feb 15;127:972-985. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.11.006. Epub 2016 Nov 5. Eur J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27837994
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel pyrazole sulfonamide derivatives as dual COX-2/5-LOX inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Mar 1;189:112066. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112066. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31982653
-
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of new pyrazoloquinazoline derivatives as dual COX-2/5-LOX inhibitors.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2020 Nov;353(11):e2000027. doi: 10.1002/ardp.202000027. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2020. PMID: 32696514
-
An integrated overview on pyrrolizines as potential anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2016 May 23;114:257-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.01.055. Epub 2016 Feb 1. Eur J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26994693 Review.
-
Licofelone--a novel analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent.Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7(3):251-63. doi: 10.2174/156802607779941305. Curr Top Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17305568 Review.
Cited by
-
Pyrrolidine in Drug Discovery: A Versatile Scaffold for Novel Biologically Active Compounds.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2021 Aug 10;379(5):34. doi: 10.1007/s41061-021-00347-5. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2021. PMID: 34373963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity of Tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine Derivatives as Anti-Inflammatory Agents.Molecules. 2017 Nov 13;22(11):1960. doi: 10.3390/molecules22111960. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29137170 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Design and Discovery: Principles and Applications.Molecules. 2017 Feb 13;22(2):279. doi: 10.3390/molecules22020279. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28208821 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacophore-based virtual screening, synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular docking study of novel pyrrolizines bearing urea/thiourea moieties with potential cytotoxicity and CDK inhibitory activities.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021 Dec;36(1):15-33. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1837124. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33103497 Free PMC article.
-
NSAIDs between past and present; a long journey towards an ideal COX-2 inhibitor lead.RSC Adv. 2024 Sep 25;14(42):30647-30661. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04686b. eCollection 2024 Sep 24. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39324041 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roberts L.J., Morrow J.D. In: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. Goodman L.S., Gilman A.G., Hardman J.G., Limbird A.E., editors. McGraw Hill; New York, NY, USA: 2001. pp. 687–733.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

