Non-Classical Monocytes and Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Correlate with Coronary Artery Calcium Progression in Chronically HIV-1 Infected Adults on Stable Antiretroviral Therapy
- PMID: 26867220
- PMCID: PMC4750941
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149143
Non-Classical Monocytes and Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Correlate with Coronary Artery Calcium Progression in Chronically HIV-1 Infected Adults on Stable Antiretroviral Therapy
Abstract
Background: Persistent inflammation and immune activation has been hypothesized to contribute to increased prevalence of subclinical atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk in patients with chronic HIV infection. In this study, we examined the correlation of peripheral monocyte subsets and soluble biomarkers of inflammation to coronary artery calcium (CAC) progression, as measured by cardiac computed tomography scan.
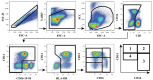
Methods: We conducted a longitudinal analysis utilizing baseline data of 78 participants with HIV infection on stable antiretroviral therapy (ART) in the Hawaii Aging with HIV-Cardiovascular study who had available baseline monocyte subset analysis as well as CAC measurement at baseline and at 2-year follow up. Monocyte phenotypes were assessed from cryopreserved blood by flow cytometry and plasma was assayed for soluble biomarkers using antibody-coated beads in a high sensitivity Milliplex Luminex platform. Change in CAC over 2 years was analyzed as the primary outcome variable.
Results: Of all monocyte subsets and biomarkers tested, higher non-classical monocyte percentage (ρ = 0.259, p = 0.022), interleukin (IL)-6 (ρ = 0.311, p = 0.012), and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 (ρ = 0.524, p = <0.001) were significantly correlated to higher 2-year CAC progression in unadjusted Spearman's correlation. Non-classical monocyte percentage (ρ = 0.247, p = 0.039), and MCP-1 (ρ = 0.487, p = <0.001), remained significantly correlated to 2-year CAC progression, while IL-6 was not (ρ = 0.209, p = 0.120) after adjustment for age, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, total/HDL cholesterol ratio, smoking history, and BMI.
Conclusion: The percentage of non-classical monocytes and plasma MCP-1 levels were independently associated with CAC progression and may be related to the progression of atherosclerosis and increased CVD risk associated with chronic HIV infection on stable ART.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and tumor necrosis factor-α levels predict the presence of coronary artery calcium in HIV-infected individuals independent of traditional cardiovascular risk factors.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2014 Feb;30(2):142-6. doi: 10.1089/AID.2013.0183. Epub 2013 Sep 21. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2014. PMID: 23984974 Free PMC article.
-
Association among plasma levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, traditional cardiovascular risk factors, and subclinical atherosclerosis.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004 Nov 2;44(9):1812-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2004.07.047. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004. PMID: 15519012
-
Non-classical monocytes predict progression of carotid artery bifurcation intima-media thickness in HIV-infected individuals on stable antiretroviral therapy.HIV Clin Trials. 2016 May;17(3):114-22. doi: 10.1080/15284336.2016.1162386. Epub 2016 Apr 4. HIV Clin Trials. 2016. PMID: 27125366 Free PMC article.
-
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and hypertension: An overview.Hipertens Riesgo Vasc. 2022 Jan-Mar;39(1):14-23. doi: 10.1016/j.hipert.2021.11.003. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Hipertens Riesgo Vasc. 2022. PMID: 34969653 Review.
-
Circulating Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 and Risk of Stroke: Meta-Analysis of Population-Based Studies Involving 17 180 Individuals.Circ Res. 2019 Sep 27;125(8):773-782. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315380. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Circ Res. 2019. PMID: 31476962 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Loss of CXCR4 on non-classical monocytes in participants of the Women's Interagency HIV Study (WIHS) with subclinical atherosclerosis.Cardiovasc Res. 2019 May 1;115(6):1029-1040. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy292. Cardiovasc Res. 2019. PMID: 30520941 Free PMC article.
-
Continued Interest and Controversy: Vitamin D in HIV.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2018 Jun;15(3):199-211. doi: 10.1007/s11904-018-0401-4. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2018. PMID: 29713871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory and immunometabolic consequences of gut dysfunction in HIV: Parallels with IBD and implications for reservoir persistence and non-AIDS comorbidities.EBioMedicine. 2019 Aug;46:522-531. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.07.027. Epub 2019 Jul 18. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31327693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex modifies the association between HIV and coronary artery disease among older adults in Uganda.J Int AIDS Soc. 2022 Jan;25(1):e25868. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25868. J Int AIDS Soc. 2022. PMID: 34995413 Free PMC article.
-
Nature versus Number: Monocytes in Cardiovascular Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 24;22(17):9119. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179119. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502027 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hansson GK. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. The New England journal of medicine. 2005;352(16):1685–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

