Gelatin-Methacryloyl Hydrogels: Towards Biofabrication-Based Tissue Repair
- PMID: 26867787
- PMCID: PMC5937681
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.01.002
Gelatin-Methacryloyl Hydrogels: Towards Biofabrication-Based Tissue Repair
Abstract
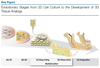
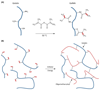
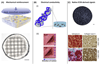
Research over the past decade on the cell-biomaterial interface has shifted to the third dimension. Besides mimicking the native extracellular environment by 3D cell culture, hydrogels offer the possibility to generate well-defined 3D biofabricated tissue analogs. In this context, gelatin-methacryloyl (gelMA) hydrogels have recently gained increased attention. This interest is sparked by the combination of the inherent bioactivity of gelatin and the physicochemical tailorability of photo-crosslinkable hydrogels. GelMA is a versatile matrix that can be used to engineer tissue analogs ranging from vasculature to cartilage and bone. Convergence of biological and biofabrication approaches is necessary to progress from merely proving cell functionality or construct shape fidelity towards regenerating tissues. GelMA has a critical pioneering role in this process and could be used to accelerate the development of clinically relevant applications.
Keywords: biofabrication; gelatin-methacryloyl; hydrogel; photo-crosslinking; regenerative medicine; tissue engineering.
Crown Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Pampaloni F, et al. The third dimension bridges the gap between cell culture and live tissue. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:839–845. - PubMed
-
- Ehrbar M, et al. Enzymatic formation of modular cell-instructive fibrin analogs for tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2007;28:3856–3866. - PubMed
-
- Occhetta P, et al. VA-086 methacrylate gelatine photopolymerizable hydrogels: a parametric study for highly biocompatible 3D cell embedding. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2014;103:2109–2117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

