MAZ mediates the cross-talk between CT-1 and NOTCH1 signaling during gliogenesis
- PMID: 26867947
- PMCID: PMC4751466
- DOI: 10.1038/srep21534
MAZ mediates the cross-talk between CT-1 and NOTCH1 signaling during gliogenesis
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: MAZ mediates the cross-talk between CT-1 and NOTCH1 signaling during gliogenesis.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 29;6:23309. doi: 10.1038/srep23309. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27023055 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
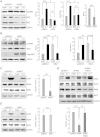
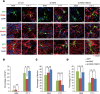
Neurons and glia cells are differentiated from neural stem/progenitor cells (NSCs/NPCs) during brain development. Concomitant activation of JAK/STAT and NOTCH1 signaling is required for gliogenesis, a process to generate glia cells to ensure proper brain functions. NOTCH1 signaling is down-regulated during neurogenesis and up-regulated during gliogenesis. However, the underlying mechanism remains elusive. We report here that cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1) activates NOTCH1 signaling through the up-regulation of ADAM10, a rate-limiting factor of NOTCH1 signaling activation. We found that a transcriptional factor, Myc-associated zinc finger protein (MAZ), plays an important role in ADAM10 transcription in response to CT-1 in NPCs. MAZ knockdown inhibits CT-1 stimulated gliogenesis and it can be rescued by over-expressing human NICD. Our results provide a link between NOTCH1 activation and neuronal secreted CT-1, suggesting that CT-1 plays an important role in ensuring the coordinated activation of NOTCH1 signaling during gliogenesis.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

