Plasma EGFR T790M ctDNA status is associated with clinical outcome in advanced NSCLC patients with acquired EGFR-TKI resistance
- PMID: 26867973
- PMCID: PMC4751431
- DOI: 10.1038/srep20913
Plasma EGFR T790M ctDNA status is associated with clinical outcome in advanced NSCLC patients with acquired EGFR-TKI resistance
Abstract
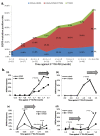
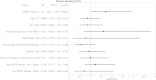
EGFR T790M mutation occurs in half of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with acquired EGFR-TKI (TKI) resistance, based on tumor re-biopsies using an invasive clinical procedure. Here, we dynamically monitored T790M mutation in circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) using serial plasma samples from NSCLC patients receiving TKI through Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) method and the associations between overall survival (OS) starting from initial TKI treatment and the T790M ctDNA status detected in plasma were analyzed. Among 318 patients, 117 who acquired TKI resistance were eligible for the analysis. T790M ctDNA was detected in the plasma of 55/117 (47%) patients. Almost half of the T790M ctDNA positive patients were identified at a median time of 2.2 months prior to clinically progressive disease (PD). Furthermore, within the patients receiving TKI treatment at 2(nd) line or later, the T790M ctDNA positive group had significantly shorter OS than the negative group (median OS: 26.9 months versus NA, P = 0.0489). Our study demonstrates the feasibility of monitoring EGFR mutation dynamics in serial plasma samples from NSCLC patients receiving TKI therapy. T790M ctDNA can be detected in plasma before and after PD as a poor prognostic factor.
Conflict of interest statement
Yes, there is potential competing financial interests. X.Y., M.Z., Y.S., G.Z. and Y.G. are employees of AstraZeneca during this study. Y.G. holds stock in AstraZeneca. D.Z. reported lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Novartis and Pfizer. J.N. reported lecture fees from Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Pfizer and F. Hoffman-La Roche. J.X. reported lecture fees from AstraZeneca, F. Hoffamn-La Roche, Eli Lilly and Pfizer. G.C. reported lecture fees from F. Hoffman-La Roche and Pfizer. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Mok T. S. et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin–paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 361, 947–957 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Maemondo M. et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non–small- cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 362, 2380–2388 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Mitsudomi T. et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations ofthe epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405):an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 11, 121–128 (2010) . - PubMed
-
- Rosell R. et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 13, 239–246 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Zhou C. et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced. Lancet Oncol 12, 735–742 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

