Randomized, blinded trial of vitamin D3 for treating aromatase inhibitor-associated musculoskeletal symptoms (AIMSS)
- PMID: 26868123
- PMCID: PMC5260816
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-016-3710-6
Randomized, blinded trial of vitamin D3 for treating aromatase inhibitor-associated musculoskeletal symptoms (AIMSS)
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Randomized, blinded trial of vitamin D3 for treating aromatase inhibitor-associated musculoskeletal symptoms (AIMSS).Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Jun;157(2):403. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-3818-8. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 27167985 No abstract available.
Abstract
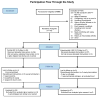
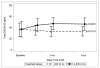
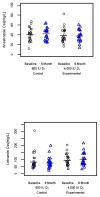
The purpose of the study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of vitamin D3 at 4000 IU/day as a treatment option for aromatase inhibitor-associated musculoskeletal symptoms (AIMSS) when compared with the usual care dose of 600 IU D3. We conducted a single site randomized, double-blind, phase 3 clinical trial in women with AIMSS comparing change in symptoms, reproductive hormones and AI pharmacokinetics. Postmenopausal women ≥18 years with stages I-IIIA breast cancer, taking AI and experiencing AIMSS [breast cancer prevention trial symptom scale-musculoskeletal (BCPT-MS) subscale ≥1.5] were admitted. Following randomization, 116 patients had a run-in period of 1 month on 600 IU D3, then began the randomized assignment to either 600 IU D3 (n = 56) or 4000 IU D3 (n = 57) daily for 6 months. The primary endpoint was a change in AIMSS from baseline (after 1 month run-in) on the BCPT-MS (general MS pain, joint pain, muscle stiffness, range for each question: 0 = not at all to 4 = extremely). Groups had no statistically significant differences demographically or clinically. There were no discernable differences between the randomly allocated treatment groups at 6 months in measures of AIMSS, pharmacokinetics of anastrozole and letrozole, serum levels of reproductive hormones, or adverse events. We found no significant changes in AIMSS measures between women who took 4000 IU D3 daily compared with 600 IU D3. The 4000 IU D3 did not adversely affect reproductive hormone levels or the steady state pharmacokinetics of anastrozole or letrozole. In both groups, serum 25(OH)D remained in the recommended range for bone health (≥30 ng/mL) and safety (<50 ng/mL).
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01509079.
Keywords: Aromatase inhibitors; Arthralgias; Breast cancer; Vitamin D3.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with Ethical Standards No conflicts of interest reported by any of the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Khan QJ, Kimler BF, Reddy PS, Sharma P, Klemp JR, Fabian CJ. Randomized trial of vitamin D3 to prevent worsening of musculoskeletal symptoms and fatigue in women with breast cancer starting adjuvant letrozole: The VITAL trial. ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 2012;30(15_suppl):9000. - PubMed
-
- Rastelli AL, Taylor ME, Gao F, Armamento-Villareal R, Jamalabadi-Majidi S, Napoli N, Ellis MJ. Vitamin D and aromatase inhibitor-induced musculoskeletal symptoms (AIMSS): a phase II, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Breast cancer research and treatment. 2011;129(1):107–116. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1644-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Prieto-Alhambra D, Javaid MK, Servitja S, Arden NK, Martinez-Garcia M, Diez-Perez A, Albanell J, Tusquets I, Nogues X. Vitamin D threshold to prevent aromatase inhibitor-induced arthralgia: a prospective cohort study. Breast cancer research and treatment. 2011;125(3):869–878. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-1075-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khan QJ, Reddy PS, Kimler BF, Sharma P, Baxa SE, O’Dea AP, Klemp JR, Fabian CJ. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels, joint pain, and fatigue in women starting adjuvant letrozole treatment for breast cancer. Breast cancer research and treatment. 2010;119(1):111–118. doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0495-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases