AdapterRemoval v2: rapid adapter trimming, identification, and read merging
- PMID: 26868221
- PMCID: PMC4751634
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-016-1900-2
AdapterRemoval v2: rapid adapter trimming, identification, and read merging
Abstract
Background: As high-throughput sequencing platforms produce longer and longer reads, sequences generated from short inserts, such as those obtained from fossil and degraded material, are increasingly expected to contain adapter sequences. Efficient adapter trimming algorithms are also needed to process the growing amount of data generated per sequencing run.
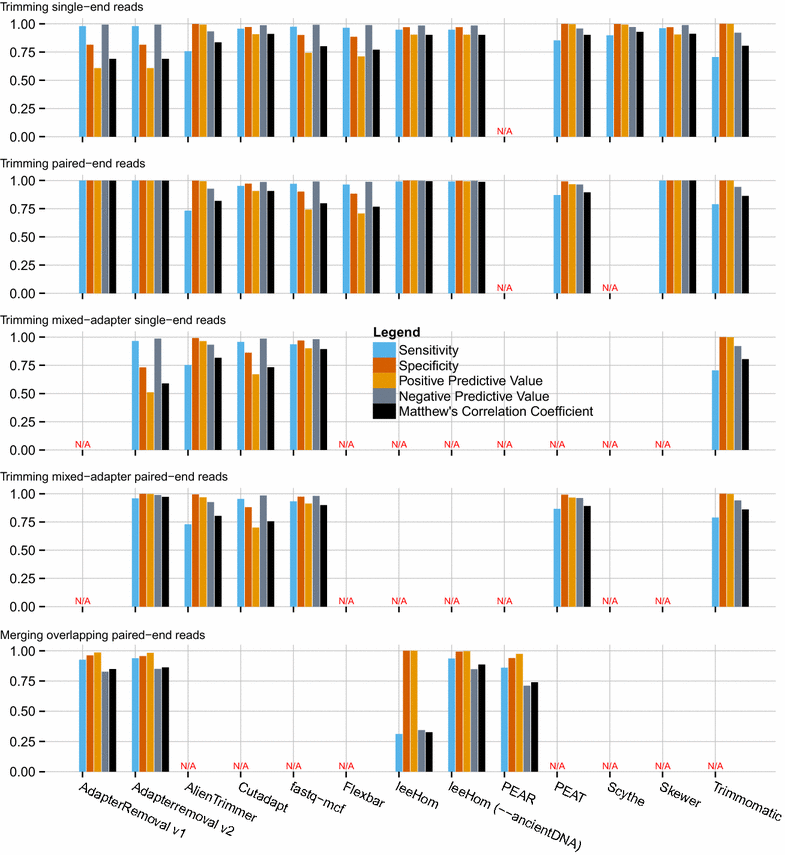
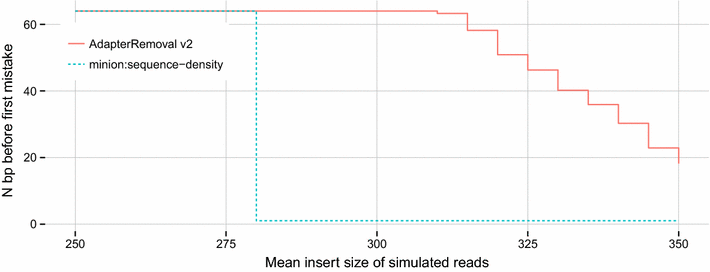
Findings: We introduce AdapterRemoval v2, a major revision of AdapterRemoval v1, which introduces (i) striking improvements in throughput, through the use of single instruction, multiple data (SIMD; SSE1 and SSE2) instructions and multi-threading support, (ii) the ability to handle datasets containing reads or read-pairs with different adapters or adapter pairs, (iii) simultaneous demultiplexing and adapter trimming, (iv) the ability to reconstruct adapter sequences from paired-end reads for poorly documented data sets, and (v) native gzip and bzip2 support.
Conclusions: We show that AdapterRemoval v2 compares favorably with existing tools, while offering superior throughput to most alternatives examined here, both for single and multi-threaded operations.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

