Does primary neoadjuvant systemic therapy eradicate minimal residual disease? Analysis of disseminated and circulating tumor cells before and after therapy
- PMID: 26868521
- PMCID: PMC4751719
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-016-0679-3
Does primary neoadjuvant systemic therapy eradicate minimal residual disease? Analysis of disseminated and circulating tumor cells before and after therapy
Abstract
Background: Patients with breast cancer (BC) undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) may experience metastatic relapse despite achieving a pathologic complete response. We analyzed patients with BC before and after NACT for disseminated tumor cells (DTCs) in the bone marrow(BM); comprehensively characterized circulating tumor cells (CTCs), including stem cell-like CTCs (slCTCs), in blood to prove the effectiveness of treatment on these cells; and correlated these findings with response to therapy, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS).
Methods: CTCs (n = 135) and slCTCs (n = 91) before and after NACT were analyzed using the AdnaTest BreastCancer, AdnaTest TumorStemCell, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (QIAGEN Hannover GmbH Germany). The expression of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and the resistance marker excision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 1 (ERCC1), nuclease were studied in separate single-plex reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction experiments. DTCs were evaluated in 142 patients before and 165 patients after NACT using the pan-cytokeratin antibody A45-B/B3 for immunocytochemistry.
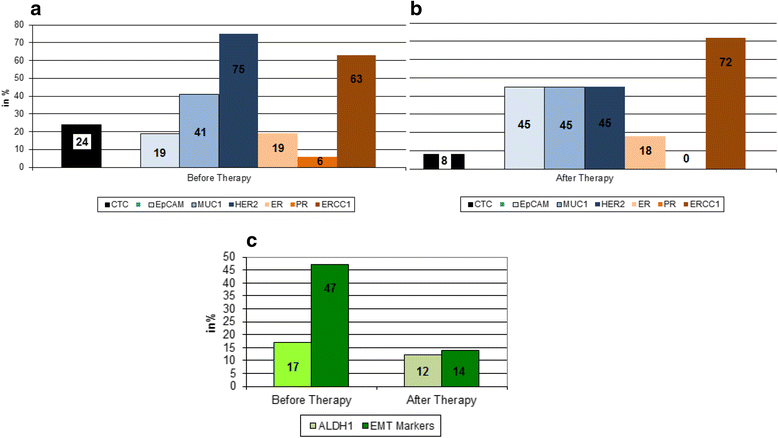
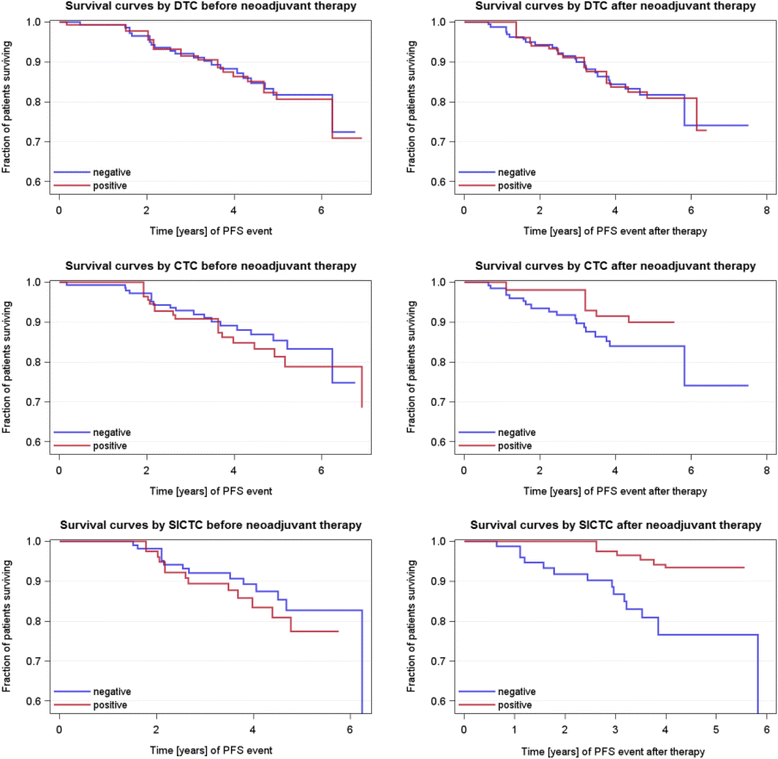
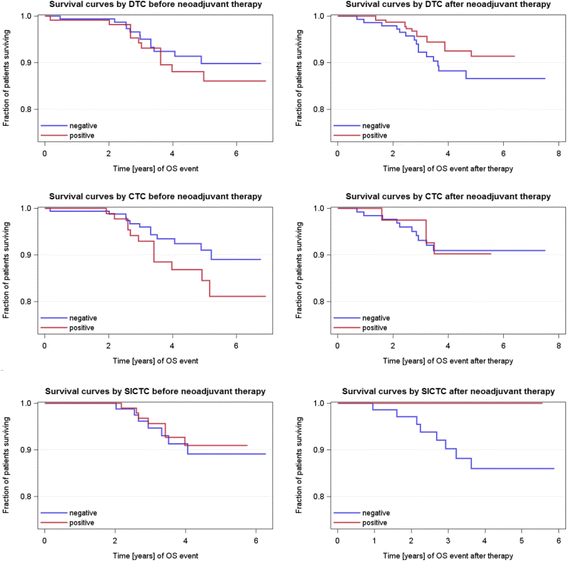
Results: The positivity rates for DTCs, CTCs, and slCTCs were 27 %, 24 %, and 51 % before and 20 %, 8 %, and 20 % after NACT, respectively. Interestingly, 72 % of CTCs present after therapy were positive for ERCC1, and CTCs before (p = 0.005) and after NACT (p = 0.05) were significantly associated with the presence of slCTCs. Whereas no significant associations with clinical parameters were found for CTCs and slCTCs, DTCs were significantly associated with nodal status (p = 0.03) and histology (0.046) before NACT and with the immunohistochemical subtype (p = 0.02) after NACT. Univariable Cox regression analysis revealed that age (p = 0.0065), tumor size before NACT (p = 0.0473), nodal status after NACT (p = 0.0137), and response to NACT (p = 0.0136) were significantly correlated with PFS, whereas age (p = 0.0162) and nodal status after NACT (p = 0.0243) were significantly associated with OS. No significant correlations were found for DTCs or any CTCs before and after therapy with regard to PFS and OS.
Conclusions: Although CTCs were eradicated more effectively than DTCs, CTCs detected after treatment seemed to be associated with tumor cells showing tumor stem cell characteristics as well as with resistant tumor cell populations that might indicate a worse outcome in the future. Thus, these patients might benefit from additional second-line treatment protocols including bisphosphonates for the eradication of DTCs.
Figures
References
-
- Kaufmann M, von Minckwitz G, Bear HD, Buzdar A, McGale P, Bonnefoi H, et al. Recommendations from an international expert panel on the use of neoadjuvant (primary) systemic treatment of operable breast cancer: new perspectives 2006. Ann Oncol. 2007;18:1927–34. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdm201. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bonnefoi H, Litière S, Piccart M, MacGrogan G, Fumoleau P, Brain E, et al. Pathological complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is an independent predictive factor irrespective of simplified breast cancer intrinsic subtypes: a landmark and two-step approach analyses from the EORTC 10994/BIG 1-00 phase III trial. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:1128–36. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu118. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

