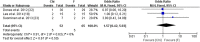Fenestrated and Chimney Technique for Juxtarenal Aortic Aneurysm: A Systematic Review and Pooled Data Analysis
- PMID: 26869488
- PMCID: PMC4751537
- DOI: 10.1038/srep20497
Fenestrated and Chimney Technique for Juxtarenal Aortic Aneurysm: A Systematic Review and Pooled Data Analysis
Abstract
Juxtarenal aortic aneurysms (JAA) account for approximately 15% of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair (FEVAR) and chimney endovascular aneurysm repair (CH-EVAR) are both effective methods to treat JAAs, but the comparative effectiveness of these treatment modalities is unclear. We searched the PubMed, Medline, Embase, and Cochrane databases to identify English language articles published between January 2005 and September 2013 on management of JAA with fenestrated and chimney techniques to conduct a systematic review to compare outcomes of patients with juxtarenal aortic aneurysm (JAA) treated with the two techniques. We compared nine F-EVAR cohort studies including 542 JAA patients and 8 CH-EVAR cohorts with 158 JAA patients regarding techniques success rates, 30-day mortality, late mortality, endoleak events and secondary intervention rates. The results of this systematic review indicate that both fenestrated and chimney techniques are attractive options for JAAs treatment with encouraging early and mid-term outcomes.
Figures
References
-
- Greenhalgh R. M. et al. United Kingdom EVAR Trial Investigators: Endovascular versus open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. N Engl J Med. 362(20), 1863–1871 (2010). - PubMed
-
- De Bruin J. L. et al. Long-term outcome of open or endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. N Engl J Med. 362(20), 1881–1889 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Prinssen M. et al. A randomized trial comparing conventional and endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 351(16), 1607–1618 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Nordon I. M. et al. Modern treatment of juxtarenal abdominal aortic aneurysms with fenestrated endografting and open repair – a systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 38(1), 35–41 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Ricotta J. J. & Oderich G. S. Fenestrated and branched stent grafts. Perspect Vasc Surg Endovasc Ther. 20(2), 174–187 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical