Disordered haematopoiesis and athero-thrombosis
- PMID: 26869607
- PMCID: PMC4823636
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv718
Disordered haematopoiesis and athero-thrombosis
Abstract
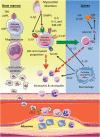
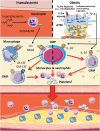
Atherosclerosis, the major underlying cause of cardiovascular disease, is characterized by a lipid-driven infiltration of inflammatory cells in large and medium arteries. Increased production and activation of monocytes, neutrophils, and platelets, driven by hypercholesterolaemia and defective high-density lipoproteins-mediated cholesterol efflux, tissue necrosis and cytokine production after myocardial infarction, or metabolic abnormalities associated with diabetes, contribute to atherogenesis and athero-thrombosis. This suggests that in addition to traditional approaches of low-density lipoproteins lowering and anti-platelet drugs, therapies directed at abnormal haematopoiesis, including anti-inflammatory agents, drugs that suppress myelopoiesis, and excessive platelet production, rHDL infusions and anti-obesity and anti-diabetic agents, may help to prevent athero-thrombosis.
Keywords: Athero-thrombosis; Atherosclerosis; Haematopoiesis; Monocytes; Neutrophils; Platelets.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author 2016. For permissions please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Gansevoort RT, Correa-Rotter R, Hemmelgarn BR, Jafar TH, Heerspink HJ, Mann JF, Matsushita K, Wen CP. Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk: epidemiology, mechanisms, and prevention. Lancet 2013;382:339–352. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 2004;351:1296–1305. - PubMed
-
- Madjid M, Miller CC, Zarubaev VV, Marinich IG, Kiselev OI, Lobzin YV, Filippov AE, Casscells SW 3rd. Influenza epidemics and acute respiratory disease activity are associated with a surge in autopsy-confirmed coronary heart disease death: results from 8 years of autopsies in 34 892 subjects. Eur Heart J 2007;28:1205–1210. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

