3D Printing for Tissue Engineering
Abstract
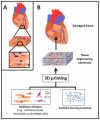
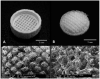
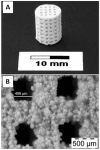
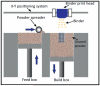
Tissue engineering aims to fabricate functional tissue for applications in regenerative medicine and drug testing. More recently, 3D printing has shown great promise in tissue fabrication with a structural control from micro- to macro-scale by using a layer-by-layer approach. Whether through scaffold-based or scaffold-free approaches, the standard for 3D printed tissue engineering constructs is to provide a biomimetic structural environment that facilitates tissue formation and promotes host tissue integration (e.g., cellular infiltration, vascularization, and active remodeling). This review will cover several approaches that have advanced the field of 3D printing through novel fabrication methods of tissue engineering constructs. It will also discuss the applications of synthetic and natural materials for 3D printing facilitated tissue fabrication.
Figures



Similar articles
-
3D Bioprinting for Vascularized Tissue Fabrication.Ann Biomed Eng. 2017 Jan;45(1):132-147. doi: 10.1007/s10439-016-1653-z. Epub 2016 May 26. Ann Biomed Eng. 2017. PMID: 27230253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three-dimensional (3D) printed scaffold and material selection for bone repair.Acta Biomater. 2019 Jan 15;84:16-33. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.11.039. Epub 2018 Nov 24. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 30481607 Review.
-
Hybrid printing of mechanically and biologically improved constructs for cartilage tissue engineering applications.Biofabrication. 2013 Mar;5(1):015001. doi: 10.1088/1758-5082/5/1/015001. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Biofabrication. 2013. PMID: 23172542
-
Recent trends in natural polysaccharide based bioinks for multiscale 3D printing in tissue regeneration: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Jul 31;183:564-588. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.04.179. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 33933542 Review.
-
A review on the use of computational methods to characterize, design, and optimize tissue engineering scaffolds, with a potential in 3D printing fabrication.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2019 Jul;107(5):1329-1351. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.34226. Epub 2018 Oct 9. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2019. PMID: 30300964 Review.
Cited by
-
Three-Dimensional Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Jun 25;10(7):759. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10070759. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of 3D Printing in Bone Grafts.Cells. 2023 Mar 10;12(6):859. doi: 10.3390/cells12060859. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36980200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D Bioprinting Stem Cell Derived Tissues.Cell Mol Bioeng. 2018 May 21;11(4):219-240. doi: 10.1007/s12195-018-0530-2. eCollection 2018 Aug. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2018. PMID: 31719887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D printed zirconia ceramic hip joint with precise structure and broad-spectrum antibacterial properties.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Jul 30;14:5977-5987. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S202457. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31534332 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of 3D Printing Technologies for Soft Materials and Potential Opportunities for Lipid-based Drug Delivery Systems.Pharm Res. 2018 Nov 7;36(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s11095-018-2531-1. Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 30406349 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
