Numerical simulation of endocytosis: Viscous flow driven by membranes with non-uniformly distributed curvature-inducing molecules
- PMID: 26869729
- PMCID: PMC4746022
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcp.2015.12.055
Numerical simulation of endocytosis: Viscous flow driven by membranes with non-uniformly distributed curvature-inducing molecules
Abstract
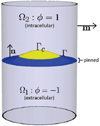
The formation of membrane vesicles from a larger membrane that occurs during endocytosis and other cell processes are typically orchestrated by curvature-inducing molecules attached to the membrane. Recent reports demonstrate that vesicles can form de novo in a few milliseconds. Membrane dynamics at these scales are strongly influenced by hydrodynamic interactions. To study this problem, we develop new diffuse interface models for the dynamics of inextensible vesicles in a viscous fluid with stiff, curvature-inducing molecules. The model couples the Navier-Stokes equations with membrane-induced bending forces that incorporate concentration-dependent bending stiffness coefficients and spontaneous curvatures, with equations for molecule transport and for a Lagrange multiplier to enforce local inextensibility. Two forms of surface transport equations are considered: Fickian surface diffusion and Cahn-Hilliard surface dynamics, with the former being more appropriate for small molecules and the latter being better for large molecules. The system is solved using adaptive finite element methods in 3D axisymmetric geometries. The results demonstrate that hydrodynamics can indeed enable the rapid formation of a small vesicle attached to the membrane by a narrow neck. When the Fickian model is used, this is a transient state with the steady state being a flat membrane with a uniformly distributed molecule concentration due to diffusion. When the Cahn-Hilliard model is used, molecule concentration gradients are sustained, the neck stabilizes and the system evolves to a steady-state with a small, compact vesicle attached to the membrane. By varying the membrane coverage of molecules in the Cahn-Hilliard model, we find that there is a critical (smallest) neck radius and a critical (fastest) budding time. These critical points are associated with changes in the vesicle morphology from spherical to mushroom-like as the molecule coverage on the membrane is increased.
Keywords: Clathrin; Endocytosis; Helfrich energy; Navier-Stokes flow; Numerical Simulation; Phase-field model.
Figures



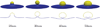

Similar articles
-
Diffuse interface models of locally inextensible vesicles in a viscous fluid.J Comput Phys. 2014 Nov 15;277:32-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2014.08.016. J Comput Phys. 2014. PMID: 25246712 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of multicomponent vesicles in a viscous fluid.J Comput Phys. 2010;229(1):119-144. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2009.09.017. J Comput Phys. 2010. PMID: 20808718 Free PMC article.
-
Boussinesq approximation of the Cahn-Hilliard-Navier-Stokes equations.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2010 Nov;82(5 Pt 2):056312. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.82.056312. Epub 2010 Nov 12. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2010. PMID: 21230581
-
Giant Vesicles Encapsulating Aqueous Two-Phase Systems: From Phase Diagrams to Membrane Shape Transformations.Front Chem. 2019 Apr 9;7:213. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00213. eCollection 2019. Front Chem. 2019. PMID: 31024898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocytosis: clathrin-mediated membrane budding.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007 Aug;19(4):417-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2007.05.003. Epub 2007 Jul 13. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17631994 Review.
Cited by
-
Hydrodynamics of transient cell-cell contact: The role of membrane permeability and active protrusion length.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Apr 25;15(4):e1006352. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006352. eCollection 2019 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 31022168 Free PMC article.
-
A general computational framework for the dynamics of single- and multi-phase vesicles and membranes.J Comput Phys. 2022 Feb 1;450:110815. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2021.110815. Epub 2021 Nov 8. J Comput Phys. 2022. PMID: 35355617 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of a multicomponent vesicle in shear flow.Soft Matter. 2017 May 21;13(19):3521-3531. doi: 10.1039/c6sm02452a. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Soft Matter. 2017. PMID: 28440378 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional morphodynamic simulations of macropinocytic cups.iScience. 2021 Oct 1;24(10):103087. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103087. eCollection 2021 Oct 22. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34755081 Free PMC article.
-
Local ligand concentration gradients induced by the plasma membrane.iScience. 2025 Jun 19;28(7):112954. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112954. eCollection 2025 Jul 18. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40687811 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aland S. Time integration for diffuse interface models for two-phase flow. J Comp. Phys. 2014;262C:58–71.
-
- Aland S, Voigt A. Benchmark computations of diffuse interface models for two-dimensional bubble dynamics. Int. J. Num. Meth. Fluids. 2012;69(3):747–761.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
