Correlation between XRCC1 Arg399Gln genetic polymorphisms and susceptibility to bladder cancer: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 26869802
- PMCID: PMC4734791
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S95658
Correlation between XRCC1 Arg399Gln genetic polymorphisms and susceptibility to bladder cancer: a meta-analysis
Abstract
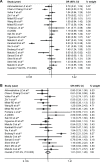
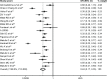
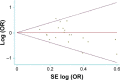
The relationship between XRCC1 polymorphisms and bladder cancer has been widely studied. Here, our meta-analysis was conducted to evaluate the correlations between common genetic polymorphisms in XRCC1 and susceptibility to bladder cancer. In order to derive a more precise estimation of the association, 27 clinical case-control studies (which met all the inclusion criteria) were included in this meta-analysis. A total of 8,539 cancer cases and 10,750 controls were involved in this meta-analysis. Overall, no significant association was detected in allelic model (A allele vs T allele odds ratio [OR] =0.87, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.71-1.06), homozygote comparison (AA vs GG OR =1.12, 95% CI, 0.68-1.85), heterozygote comparison (AT vs TT OR =1.01, 95% CI, 0.81-1.26), dominant model (AA + AG vs GG OR =0.93, 95% CI, 0.85-1.02), and recessive model (AA vs AG + GG OR =1.01, 95% CI, 0.88-1.15), but a moderately significant association was found for AG vs GG (OR =0.241, 95% CI =0.17-0.35). Subgroup analysis based on ethnicity. Ethnicity analysis suggested that genetic polymorphisms in XRCC1 were not correlated with increased bladder cancer risk among Asians (all P>0.05). Therefore, we concluded that XRCC1 genetic polymorphism may not contribute to bladder cancer susceptibility in the present meta-analysis, and further well-designed studies with a large sample size are warranted to validate our conclusion.
Keywords: XRCC1; bladder cancer; genetic polymorphism; meta-analysis; susceptibility.
Figures

References
-
- Murta-Nascimento C, Schmitz-Drager BJ, Zeegers MP, et al. Epidemiology of urinary bladder cancer: from tumor development to patient’s death. World J Urol. 2007;25(3):285–295. - PubMed
-
- Kogevinas M, ‘t Mannetje A, Cordier S, et al. Occupation and bladder cancer among men in Western Europe. Cancer Causes Control. 2003;14(10):907–914. - PubMed
-
- Zeegers MP, Tan FE, Dorant E, van Den Brandt PA. The impact of characteristics of cigarette smoking on urinary tract cancer risk: a meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies. Cancer. 2000;89(3):630–639. - PubMed
-
- Helzlsouer KJ, Harris EL, Parshad R, Perry HR, Price FM, Sanford KK. DNA repair proficiency: potential susceptibility factor for breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996;88(11):754–755. - PubMed
-
- Wei Q, Spitz MR. The role of DNA repair capacity in susceptibility to lung cancer: a review. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1997;16(3–4):295–307. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

