Clinical use of extended-release oral treprostinil in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 26869810
- PMCID: PMC4734815
- DOI: 10.2147/IBPC.S68230
Clinical use of extended-release oral treprostinil in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
The development of parenteral prostacyclin therapy marked a dramatic breakthrough in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Intravenous (IV) epoprostenol was the first PAH specific therapy and to date, remains the only treatment to demonstrate a mortality benefit. Because of the inherent complexities and risks of treating patients with continuous infusion IV therapy, there is great interest in the development of an oral prostacyclin analog that could mimic the benefits of IV therapy. Herein, we highlight the development of oral prostacyclin therapy, focusing on oral treprostinil, the only US Food and Drug Administration approved oral prostacyclin. Recent Phase III clinical trials have shown the drug to improve exercise tolerance in treatment-naïve PAH patients, but not patients on background oral therapy. Oral treprostinil appears to be most efficacious at higher doses, but its side effect profile and complexities with dosing complicate its use. While oral treprostinil's current therapeutic role in PAH remains unclear, ongoing studies of this class of medication should help clarify their role in the treatment of PAH.
Keywords: oral treprostinil; pulmonary arterial hypertension; selexipag.
Figures
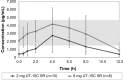
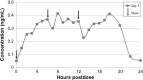
References
-
- Romberg E. Uebere Sklerose der Lungenarterien. Dtsch Arch Klin Med. 1891;48:197–206. German.
-
- Dresdale DT, Schultz M, Michtom RJ. Primary pulmonary hypertension. I. Clinical and hemodynamic study. Am J Med. 1951;11(6):686–705. - PubMed
-
- Barst RJ, Rubin LJ, Long WA, et al. A comparison of continuous intravenous epoprostenol (prostacyclin) with conventional therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(5):296–301. - PubMed
-
- Moncada S, Gryglewski R, Bunting S, Vane JR. An enzyme isolated from arteries transforms prostaglandin endoperoxides to an unstable substance that inhibits platelet aggregation. Nature. 1976;263(5579):663–665. - PubMed
-
- Farber HW, Loscalzo J. Pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(16):1655–1665. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

