Protective effect of wild ginseng cambial meristematic cells on d-galactosamine-induced hepatotoxicity in rats
- PMID: 26869831
- PMCID: PMC4593786
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2015.04.002
Protective effect of wild ginseng cambial meristematic cells on d-galactosamine-induced hepatotoxicity in rats
Abstract
Background: Panax ginseng has a wide range of biological activities including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory functions. Wild ginseng cambial meristematic cells (CMCs) were obtained from P. ginseng cambium. This study examined the protective mechanism of wild ginseng CMCs against d-galactosamine (GalN)-induced liver injury. GalN, a well-known hepatotoxicant, causes severe hepatocellular inflammatory damage and clinical features similar to those of human viral hepatitis in experimental animals.
Methods: Hepatotoxicity was induced in rats using GalN (700 mg/kg, i.p.). Wild ginseng CMCs was administered orally once a day for 2 wks, and then 2 h prior to and 6 h after GalN injection.
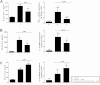
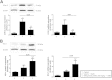
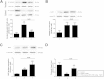
Results: Wild ginseng CMCs attenuated the increase in serum aminotransferase activity that occurs 24 h after GalN injection. Wild ginseng CMCs also attenuated the GalN-induced increase in serum tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6 level, and hepatic cyclooxygenase-2 protein and mRNA expression. Wild ginseng CMCs augmented the increase in serum interleukin -10 and hepatic heme oxygenase-1 protein and mRNA expression that was induced by GalN, inhibited the increase in the nuclear level of nuclear factor-kappa B, and enhanced the increase in NF-E2-related factor 2.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that wild ginseng CMCs protects liver against GalN-induced inflammation by suppressing proinflammatory mediators and enhancing production of anti-inflammatory mediators.
Keywords: Panax ginseng; d-galactosamine; heme oxygenase-1; hepatitis; wild ginseng cambial meristematic cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protective Effects of Sesquiterpenoids from the Root of Panax ginseng on Fulminant Liver Injury Induced by Lipopolysaccharide/d-Galactosamine.J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Jul 25;66(29):7758-7763. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b02627. Epub 2018 Jul 16. J Agric Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 29974747
-
Wild ginseng cambial meristematic cells ameliorate hepatic steatosis and mitochondrial dysfunction in high-fat diet-fed mice.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2016 Jan;68(1):119-27. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12487. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26806698
-
Protective effects of Mg-CUD against D-galactosamine-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Apr 25;657(1-3):138-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.01.030. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21284943
-
Protective effects of HV-P411 complex against D-galactosamine-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.Am J Chin Med. 2012;40(3):467-80. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X1250036X. Am J Chin Med. 2012. PMID: 22745064
-
Cambial meristematic cell culture: a sustainable technology toward in vitro specialized metabolites production.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2023 Dec;43(5):734-752. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2022.2055995. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 35658789 Review.
Cited by
-
Panax Ginseng Induces Toxic Hepatitis and Acute Kidney Injury.Chonnam Med J. 2017 May;53(2):168-169. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2017.53.2.168. Epub 2017 May 25. Chonnam Med J. 2017. PMID: 28584797 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effectiveness and Safety of Panax ginseng Extract on Hepatic Dysfunction: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Jul 16;2020:2689565. doi: 10.1155/2020/2689565. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32724321 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism and research progress on pharmacology of traditional Chinese medicine in liver injury.Pharm Biol. 2018 Dec;56(1):594-611. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2018.1517185. Pharm Biol. 2018. PMID: 31070528 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bernal W., Auzinger G., Dhawan A., Wendon J. Acute liver failure. Lancet. 2010;376:190–201. - PubMed
-
- Decker K., Keppler D. Galactosamine hepatitis: key role of the nucleotide deficiency period in the pathogenesis of cell injury and cell death. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1974;71:77–106. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh M., Das J., Sil P.C. D(+) galactosamine induced oxidative and nitrosative stress-mediated renal damage in rats via NF-kappaB and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) pathways is ameliorated by a polyphenol xanthone, mangiferin. Free Radic Res. 2012;46:116–132. - PubMed
-
- Immenschuh S., Baumgart-Vogt E., Mueller S. Heme oxygenase-1 and iron in liver inflammation: a complex alliance. Curr Drug Targets. 2010;11:1541–1550. - PubMed
-
- Shukla R., Kumar M. Role of Panax ginseng as an antioxidant after cadmium-induced hepatic injuries. Food Chem Toxicol. 2009;47:769–773. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

