Characterization of Korean Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer): History, preparation method, and chemical composition
- PMID: 26869832
- PMCID: PMC4593794
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2015.04.009
Characterization of Korean Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer): History, preparation method, and chemical composition
Abstract
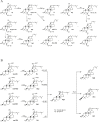
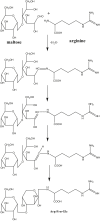
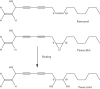
It has been reported that Korean Red Ginseng has been manufactured for 1,123 y as described in the GoRyeoDoGyeong record. The Korean Red Ginseng manufactured by the traditional preparation method has its own chemical component characteristics. The ginsenoside content of the red ginseng is shown as Rg1: 3.3 mg/g, Re: 2.0 mg/g, Rb1: 5.8 mg/g, Rc:1.7 mg/g, Rb2: 2.3 mg/g, and Rd: 0.4 mg/g, respectively. It is known that Korean ginseng generally consists of the main root and the lateral or fine roots at a ratio of about 75:25. Therefore, the red ginseng extract is prepared by using this same ratio of the main root and lateral or fine roots and processed by the historical traditional medicine prescription. The red ginseng extract is prepared through a water extraction (90(°)C for 14-16 h) and concentration process (until its final concentration is 70-73 Brix at 50-60(°)C). The ginsenoside contents of the red ginseng extract are shown as Rg1: 1.3 mg/g, Re: 1.3 mg/g, Rb1: 6.4 mg/g, Rc:2.5 mg/g, Rb2: 2.3 mg/g, and Rd: 0.9 mg/g, respectively. Arginine-fructose-glucose (AFG) is a specific amino-sugar that can be produced by chemical reaction of the process when the fresh ginseng is converted to red ginseng. The content of AFG is 1.0-1.5% in red ginseng. Acidic polysaccharide, which has been known as an immune activator, is at levels of 4.5-7.5% in red ginseng. Therefore, we recommended that the chemical profiles of Korean Red Ginseng made through the defined traditional method should be well preserved and it has had its own chemical characteristics since its traditional development.
Keywords: Red ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer); chemical components; historical document; preparation methods.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Change of Ginsenoside Profiles in Processed Ginseng by Drying, Steaming, and Puffing.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Feb 28;29(2):222-229. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1809.09056. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30609886
-
In situ analysis of chemical components induced by steaming between fresh ginseng, steamed ginseng, and red ginseng.J Ginseng Res. 2017 Jul;41(3):361-369. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2016.07.004. Epub 2016 Jul 20. J Ginseng Res. 2017. PMID: 28701878 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Ginsenoside Contents in Different Parts of Korean Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer).Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2016 Dec;21(4):389-392. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2016.21.4.389. Epub 2016 Dec 31. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2016. PMID: 28078264 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the pharmacological effects of Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolium.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2008 Sep;29(9):1103-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00868.x. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2008. PMID: 18718179 Review.
-
Anticarcinogenic effect of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer and identification of active compounds.J Korean Med Sci. 2001 Dec;16 Suppl(Suppl):S6-18. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2001.16.S.S6. J Korean Med Sci. 2001. PMID: 11748383 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of gut microbiota on the pharmacokinetics of protopanaxadiol ginsenosides Rd, Rg3, F2, and compound K in healthy volunteers treated orally with red ginseng.J Ginseng Res. 2020 Jul;44(4):611-618. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2019.05.012. Epub 2019 Jun 5. J Ginseng Res. 2020. PMID: 32617041 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive Gliosis Contributes to Nrf2-Dependent Neuroprotection by Pretreatment with Dimethyl Fumarate or Korean Red Ginseng Against Hypoxic-Ischemia: Focus on Hippocampal Injury.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Jan;57(1):105-117. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01760-0. Epub 2019 Sep 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 31494826 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment with Korean red ginseng or dimethyl fumarate attenuates reactive gliosis and confers sustained neuroprotection against cerebral hypoxic-ischemic damage by an Nrf2-dependent mechanism.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Feb 1;131:98-114. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.11.017. Epub 2018 Nov 17. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30458277 Free PMC article.
-
Ginsenoside Rb1 exerts antiarrhythmic effects by inhibiting INa and ICaL in rabbit ventricular myocytes.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 31;9(1):20425. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-57010-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31892729 Free PMC article.
-
Extension of Drosophila lifespan by Korean red ginseng through a mechanism dependent on dSir2 and insulin/IGF-1 signaling.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Oct 31;11(21):9369-9387. doi: 10.18632/aging.102387. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31672931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brekhman I.I., Dardymov I.V. New substances of plant origin which increase nonspecific resistance. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1969;9:419–430. - PubMed
-
- Liu C.X., Xio P.G. Recent advances on ginseng research in China. J Ethnopharmacol. 1992;35:27–38. - PubMed
-
- Wang J., Li S.S., Fan Y.Y., Chen Y., Liu D., Cheng H.R., Gao X.G., Zhou Y.F. Anti-fatigue activity of the water-soluble polysaccharides isolated from Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010;130:421–423. - PubMed
-
- Babiker L.B., Gadkariem E.A., Alashban R.M., Aljohar H.I. Investigation of stability of Korean ginseng in herbal drug product. Am J Appl Sci. 2014;11:160–170.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

