Synergistic effects of nitric oxide and exercise on revascularisation in the infarcted ventricle in a murine model of myocardial infarction
- PMID: 26869868
- PMCID: PMC4746998
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2015-510
Synergistic effects of nitric oxide and exercise on revascularisation in the infarcted ventricle in a murine model of myocardial infarction
Abstract
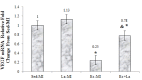
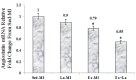
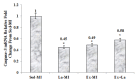
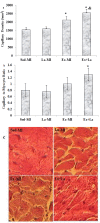
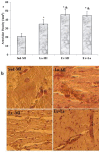
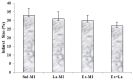
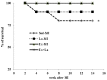
It has been shown that density of microvessels decreases in the left ventricular after myocardial infarction (MI). The change of angiogenic and angiostatic factors as the main factors in revascularisation after exercise training in area at risk is not determined yet in MI. Therefore, the aim of the present study was the effect of exercise training and L-arginine supplementation on area at risk angiogenesis in myocardial infarction rat. Four weeks after surgery (Left Anterior Descending Coronary artery Ligation), myocardial infarction rats were divided into 4 groups: Sedentary rats (Sed-MI); L-arginine supplementation (La-MI); Exercise training (Ex-MI) and Exercise + L-arginine (Ex+La). Exercise training (ET) lasted for 10 weeks at 17 m/min for 10-50 min day(-1). Rats in the L-arginine-treated groups drank water containing 4 % L-arginine. After ET and L-arginine supplementation, ventricular function was evaluated and angiogenic and angiostatic indices were measured at ~1 mm from the edge of scar tissue (area at risk). Statistical analysis revealed that gene expression of VEGF as an angiogenic factor, angiostatin as an angiostatic factor and caspase-3 at area at risk decrease significantly in response to exercise training compared to the sedentary group. The capillary and arteriolar density in the Ex groups were significantly higher than those of the Sed groups. Compared to the Ex-MI group, the Ex+La group showed a markedly increase in capillary to fiber ratio. No significant differences were found in infarct size among the four groups, but cardiac function increased in response to exercise. Exercise training increases revascularization at area at risk by reduction of angiostatin. L-arginine supplementation causes additional effects on exercise-induced angiogenesis by preventing more reduction of VEGF gene expression in response to exercise. These improvements, in turn, increase left ventricular systolic function and decrease mortality in myocardial infarction rats.
Keywords: L-arginine; angiogenesis; cardiac function; exercise training; myocardial infarction.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Aerobic training and l-arginine supplementation promotes rat heart and hindleg muscles arteriogenesis after myocardial infarction.J Physiol Biochem. 2016 Sep;72(3):393-404. doi: 10.1007/s13105-016-0480-x. Epub 2016 Apr 27. J Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27121159
-
Effect of Exercise Training and L-arginine on Oxidative Stress and Left Ventricular Function in the Post-ischemic Failing Rat Heart.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2016 Apr;16(2):122-9. doi: 10.1007/s12012-015-9319-x. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 25762197
-
Aerobic training and L-arginine supplement attenuates myocardial infarction-induced kidney and liver injury in rats via reduced oxidative stress.Indian Heart J. 2018 Jul-Aug;70(4):538-543. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2017.08.011. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Indian Heart J. 2018. PMID: 30170650 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of different initiation time of exercise training on left ventricular remodeling and cardiopulmonary rehabilitation in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction.Disabil Rehabil. 2016;38(3):268-76. doi: 10.3109/09638288.2015.1036174. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Disabil Rehabil. 2016. PMID: 25885667 Review.
-
The Beneficial Role of Exercise Training for Myocardial Infarction Treatment in Elderly.Front Physiol. 2020 Apr 24;11:270. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00270. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32390856 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the preconditioning effect of different exercise training modalities on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 5;18(12):e0295169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295169. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38051732 Free PMC article.
-
Preconditioning Effect of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) and Berberine Supplementation on the Gene Expression of Angiogenesis Regulators and Caspase-3 Protein in the Rats with Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion (IR) Injury.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Sep 4;2020:4104965. doi: 10.1155/2020/4104965. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32964031 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the effect of 8 weeks of high-intensity interval training and berberine supplementation on some echocardiography and electrocardiogram indices following myocardial ischemia-reperfusion in rats.ARYA Atheroscler. 2022 Jul;18(4):1-9. doi: 10.22122/arya.2022.26274. ARYA Atheroscler. 2022. PMID: 36817350 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of memantine nitrates as a potential treatment for neurodegenerative diseases.Medchemcomm. 2016 Oct 20;8(1):135-147. doi: 10.1039/c6md00509h. eCollection 2017 Jan 1. Medchemcomm. 2016. PMID: 30108699 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial angiogenesis induced by concurrent vitamin D supplementation and aerobic-resistance training is mediated by inhibiting miRNA-15a, and miRNA-146a and upregulating VEGF/PI3K/eNOS signaling pathway.Pflugers Arch. 2023 Apr;475(4):541-555. doi: 10.1007/s00424-023-02788-x. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Pflugers Arch. 2023. PMID: 36689014
References
-
- Briet F, Keith M, Leong-Poi H, Kadakia A, Aba-Alkhail K, Giliberto J-P, et al. Triple nutrient supplementation improves survival, infarct size and cardiac function following myocardial infarction in rats. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2008;18:691–699. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
