Design and Analysis of a Neuromemristive Reservoir Computing Architecture for Biosignal Processing
- PMID: 26869876
- PMCID: PMC4740959
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00502
Design and Analysis of a Neuromemristive Reservoir Computing Architecture for Biosignal Processing
Abstract
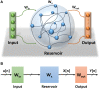
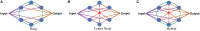
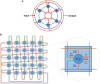
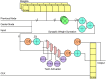
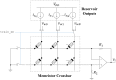
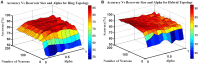
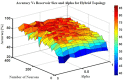
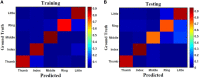
Reservoir computing (RC) is gaining traction in several signal processing domains, owing to its non-linear stateful computation, spatiotemporal encoding, and reduced training complexity over recurrent neural networks (RNNs). Previous studies have shown the effectiveness of software-based RCs for a wide spectrum of applications. A parallel body of work indicates that realizing RNN architectures using custom integrated circuits and reconfigurable hardware platforms yields significant improvements in power and latency. In this research, we propose a neuromemristive RC architecture, with doubly twisted toroidal structure, that is validated for biosignal processing applications. We exploit the device mismatch to implement the random weight distributions within the reservoir and propose mixed-signal subthreshold circuits for energy efficiency. A comprehensive analysis is performed to compare the efficiency of the neuromemristive RC architecture in both digital(reconfigurable) and subthreshold mixed-signal realizations. Both Electroencephalogram (EEG) and Electromyogram (EMG) biosignal benchmarks are used for validating the RC designs. The proposed RC architecture demonstrated an accuracy of 90 and 84% for epileptic seizure detection and EMG prosthetic finger control, respectively.
Keywords: EMG signal processing; epileptic seizure detection and prediction; memristors; neuromemristive systems; neuromorphic; neuromorphic hardware; process variations; reservoir computing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Andrzejak R. G., Lehnertz K., Mormann F., Rieke C., David P., Elger C. E. (2001). Indications of nonlinear deterministic and finite-dimensional structures in time series of brain electrical activity: dependence on recording region and brain state. Phys. Rev. E 64:061907. 10.1103/PhysRevE.64.061907 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Buzsaki G. (2006). Rhythms of the Brain. New York, NY: Oxford University Press, Inc. 10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195301069.001.0001 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

