Brain and Retinal Pericytes: Origin, Function and Role
- PMID: 26869887
- PMCID: PMC4740376
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00020
Brain and Retinal Pericytes: Origin, Function and Role
Abstract
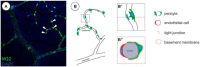
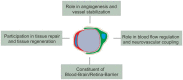
Pericytes are specialized mural cells located at the abluminal surface of capillary blood vessels, embedded within the basement membrane. In the vascular network these multifunctional cells fulfil diverse functions, which are indispensable for proper homoeostasis. They serve as microvascular stabilizers, are potential regulators of microvascular blood flow and have a central role in angiogenesis, as they for example regulate endothelial cell proliferation. Furthermore, pericytes, as part of the neurovascular unit, are a major component of the blood-retina/brain barrier. CNS pericytes are a heterogenic cell population derived from mesodermal and neuro-ectodermal germ layers acting as modulators of stromal and niche environmental properties. In addition, they display multipotent differentiation potential making them an intriguing target for regenerative therapies. Pericyte-deficiencies can be cause or consequence of many kinds of diseases. In diabetes, for instance, pericyte-loss is a severe pathological process in diabetic retinopathy (DR) with detrimental consequences for eye sight in millions of patients. In this review, we provide an overview of our current understanding of CNS pericyte origin and function, with a special focus on the retina in the healthy and diseased. Finally, we highlight the role of pericytes in de- and regenerative processes.
Keywords: blood flow regulation; blood retina barrier; pericytes; retinal diseases; tissue regeneration.
Figures

References
-
- André P., Saubaméa B., Cochois-Guégan V., Marie-Claire C., Cattelotte J., Smirnova M., et al. (2012). Transport of biogenic amine neurotransmitters at the mouse blood-retina and blood-brain barriers by uptake1 and uptake2. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 32, 1989–2001. 10.1038/jcbfm.2012.109 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

