Bacterial Toxins as Pathogen Weapons Against Phagocytes
- PMID: 26870008
- PMCID: PMC4734073
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00042
Bacterial Toxins as Pathogen Weapons Against Phagocytes
Abstract
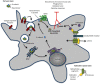
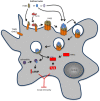
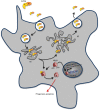
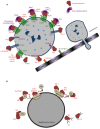
Bacterial toxins are virulence factors that manipulate host cell functions and take over the control of vital processes of living organisms to favor microbial infection. Some toxins directly target innate immune cells, thereby annihilating a major branch of the host immune response. In this review we will focus on bacterial toxins that act from the extracellular milieu and hinder the function of macrophages and neutrophils. In particular, we will concentrate on toxins from Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria that manipulate cell signaling or induce cell death by either imposing direct damage to the host cells cytoplasmic membrane or enzymatically modifying key eukaryotic targets. Outcomes regarding pathogen dissemination, host damage and disease progression will be discussed.
Keywords: bacterial exotoxin; immunomodulation; innate immune response; macrophage; neutrophil; phagocyte.
Figures

References
-
- Adusumilli S., Mve-Obiang A., Sparer T., Meyers W., Hayman J., Small P. L. (2005). Mycobacterium ulcerans toxic macrolide, mycolactone modulates the host immune response and cellular location of M. ulcerans in vitro and in vivo. Cell. Microbiol. 7 1295–1304. 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00557.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

