Efficient Rutin and Quercetin Biosynthesis through Flavonoids-Related Gene Expression in Fagopyrum tataricum Gaertn. Hairy Root Cultures with UV-B Irradiation
- PMID: 26870075
- PMCID: PMC4740399
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00063
Efficient Rutin and Quercetin Biosynthesis through Flavonoids-Related Gene Expression in Fagopyrum tataricum Gaertn. Hairy Root Cultures with UV-B Irradiation
Abstract
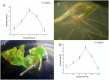
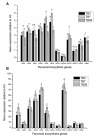
Transformed hairy roots had been efficiently induced from the seedlings of Fagopyrum tataricum Gaertn. due to the infection of Agrobacterium rhizogenes. Hairy roots were able to display active elongation with high root branching in 1/2 MS medium without growth regulators. The stable introduction of rolB and aux1 genes of A. rhizogenes WT strain 15834 into F. tataricum plants was confirmed by PCR analysis. Besides, the absence of virD gene confirmed hairy root was bacteria-free. After six different media and different sources of concentration were tested, the culturing of TB7 hairy root line in 1/2 MS liquid medium supplemented with 30 g l(-1) sucrose for 20 days resulted in a maximal biomass accumulation (13.5 g l(-1) fresh weight, 1.78 g l(-1) dry weight) and rutin content (0.85 mg g(-1)). The suspension culture of hairy roots led to a 45-fold biomass increase and a 4.11-fold rutin content increase in comparison with the suspension culture of non-transformed roots. The transformation frequency was enhanced through preculturing for 2 days followed by infection for 20 min. The UV-B stress treatment of hairy roots resulted in a striking increase of rutin and quercetin production. Furthermore, the hairy root lines of TB3, TB7, and TB28 were chosen to study the specific effects of UV-B on flavonoid accumulation and flavonoid biosynthetic gene expression by qRT-PCR. This study has demonstrated that the UV-B radiation was an effective elicitor that dramatically changed in the transcript abundance of ftpAL, FtCHI, FtCHS, FtF3H, and FtFLS-1 in F. tataricum hairy roots.
Keywords: UV-B; flavonoid biosynthetic genes; genetic transformation; hairy root; rutin; tartary buckwheat.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

