High mobility group box 1 regulates tumor metastasis in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma via the PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways
- PMID: 26870167
- PMCID: PMC4727160
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2015.3843
High mobility group box 1 regulates tumor metastasis in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma via the PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways
Abstract
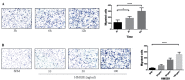
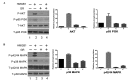
The present study examined the mechanisms of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1)-induced cell migration in human cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) SCC13 cells. Western blotting, a chemotaxis assay and ELISA were performed to analyze HMGB1 level in SCC13 cells and its ability to regulate tumor metastasis. The results demonstrated a significantly higher level of HMGB1 in the SCC13 cell supernatant compared with the human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cell supernatant. Administration of HMGB1 to the SCC13 cells caused cell migration, which occurred in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Moreover, HMGB1 significantly activated the phosphosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways by an increased level of phosphorylation in p85PI3K, AKT, p38 and p42/44 MAPK. Taken together, these data suggest that HMGB1 regulates tumor metastasis in CSCC via the PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways.
Keywords: HMGB1; MAPK pathway; PI3K/AKT pathway; cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma; migration.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long noncoding RNA LINC00520 prevents the progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma through the inactivation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by downregulating EGFR.Chin Med J (Engl). 2019 Feb;132(4):454-465. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000070. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019. PMID: 30707166 Free PMC article.
-
Plumbagin induces G2/M arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy via p38 MAPK- and PI3K/Akt/mTOR-mediated pathways in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Mar 16;9:1601-26. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S76057. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25834400 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of fucosyltransferase IV promotes A431 cell proliferation through activating MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Nov;225(2):612-9. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22250. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20506505
-
High mobility group box 1 protein attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury via inhibition of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Aug;14(2):1582-1588. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4653. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28810624 Free PMC article.
-
High-Mobility Group Box 1 Mediates Fibroblast Activity via RAGE-MAPK and NF-κB Signaling in Keloid Scar Formation.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 28;19(1):76. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010076. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29283384 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in squamous cell carcinoma with an especial focus on head and neck cancers.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Aug 13;22(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02676-x. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 35964082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HMGB1 is negatively correlated with the development of endometrial carcinoma and prevents cancer cell invasion and metastasis by inhibiting the process of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.Onco Targets Ther. 2017 Mar 3;10:1389-1402. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S123085. eCollection 2017. Onco Targets Ther. 2017. PMID: 28424555 Free PMC article.
-
VCP interaction with HMGB1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.J Transl Med. 2022 May 13;20(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03416-5. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35562734 Free PMC article.
-
FABP7 inhibits proliferation and invasion abilities of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cells via the Notch signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2022 Jun 10;24(2):254. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13374. eCollection 2022 Aug. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35765272 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Skin Cancers: A Review.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2019 Dec 16;2019:3851576. doi: 10.1155/2019/3851576. eCollection 2019. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2019. PMID: 31934531 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
