Expression of pigment epithelium-derived factor is associated with a good prognosis and is correlated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related genes in infiltrating ductal breast carcinoma
- PMID: 26870178
- PMCID: PMC4727170
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2015.3880
Expression of pigment epithelium-derived factor is associated with a good prognosis and is correlated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related genes in infiltrating ductal breast carcinoma
Abstract
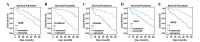
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a pivotal event in the progression of cancer towards metastasis. Given that pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) inhibits angiogenesis, the present study analyzed whether PEDF expression is associated with EMT and prognosis in invasive ductal breast cancer (IDC). Immunohistochemical analysis was used to examine the expression levels of PEDF, E-cadherin, vimentin, Snail and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) in 119 cases of IDC. Correlations between PEDF expression and EMT-related genes, and clinicopathological features and clinical prognosis were analyzed. E-cadherin, vimentin, Snail and NF-κB expression was correlated with tumor size, lymph node metastasis and clinicopathological stage. PEDF expression was closely associated with tumor size. Spearman's rank correlation analysis revealed a positive correlation between PEDF and E-cadherin, vimentin, Snail and NF-κB expression (P<0.05). Additionally, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis demonstrated that the five-year survival rate was higher for patients with PEDF- and E-cadherin-positive tumors, but was lower for those with vimentin-, Snail- and NF-κB-positive tumors. Vimentin, E-cadherin and NF-κB levels were dependent prognostic factors of favorable outcomes in IDC, as determined by Cox multivariate analysis. PEDF expression in breast cancer was significantly associated with EMT-related genes, suggesting that it may be an EMT suppressor. However, its potential as a prognostic indicator in breast cancer warrants further investigation.
Keywords: breast cancer; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; pigment epithelium-derived factor; prognosis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pigment Epithelial-Derived Factor in Pancreatic and Liver Cancers-From Inflammation to Cancer.Biomedicines. 2024 Oct 4;12(10):2260. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102260. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory effects of pigment epithelium-derived factor on epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion of breast cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Oct 1;10(10):10593-10602. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966401 Free PMC article.
-
[Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits metastasis and invasion of breast cancer via regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2018 Jan 30;38(1):1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2018.01.01. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2018. PMID: 33177035 Chinese.
-
Downregulation of pigment epithelium-derived factor is associated with increased epithelial-mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer.Panminerva Med. 2017 Mar;59(1):9-14. doi: 10.23736/S0031-0808.16.03179-7. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Panminerva Med. 2017. PMID: 27644257
-
The novel role of Yin Yang 1 in the regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in cancer via the dysregulated NF-κB/Snail/YY1/RKIP/PTEN Circuitry.Crit Rev Oncog. 2011;16(3-4):211-26. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.v16.i3-4.50. Crit Rev Oncog. 2011. PMID: 22248055 Review.
Cited by
-
Upregulation of PEDF Predicts a Poor Prognosis and Promotes Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression by Modulating the MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 26;11:625612. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.625612. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33718190 Free PMC article.
-
Pigment epithelium-derived factor promotes peritoneal dissemination of ovarian cancer through induction of immunosuppressive macrophages.Commun Biol. 2022 Sep 2;5(1):904. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03837-4. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36056141 Free PMC article.
-
Pigment Epithelial-Derived Factor in Pancreatic and Liver Cancers-From Inflammation to Cancer.Biomedicines. 2024 Oct 4;12(10):2260. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102260. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of pigment epithelium derived factor expression with cancer progression and prognosis: a meta-analysis study.Discov Oncol. 2021 Dec 15;12(1):61. doi: 10.1007/s12672-021-00457-y. Discov Oncol. 2021. PMID: 35201465 Free PMC article.
-
NFκB-Mediated Mechanisms Drive PEDF Expression and Function in Pre- and Post-Menopausal Oestrogen Levels in Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 9;23(24):15641. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415641. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555293 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
