MicroRNA-101 suppresses migration and invasion via targeting vascular endothelial growth factor-C in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- PMID: 26870229
- PMCID: PMC4727073
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2015.3832
MicroRNA-101 suppresses migration and invasion via targeting vascular endothelial growth factor-C in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Abstract
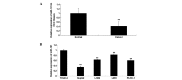
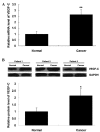
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of non-coding RNAs 18-25 nucleotides in length, which play important roles in the regulation of cancer progression through gene silencing. miRNA (miR)-101 has been suggested to be associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the detailed role of miR-101 in HCC metastasis and the underlying mechanism remain largely unclear. The present study demonstrated that the expression of miR-101 was significantly reduced in HCC tissues compared with that in matched normal adjacent tissues. miR-101 was also found to be downregulated in four HCC cell lines compared with its expression in a normal liver cell line. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C was further identified as a direct target of miR-101, and the protein expression of VEGF-C was downregulated by miR-101 in HepG2 HCC cells. Furthermore, the overexpression of miR-101 and the knockdown of VEGF-C significantly inhibited HepG2 cell migration and invasion, while restoration of VEGF-C reversed the inhibitory effect of miR-101 overexpression on HepG2 cell migration and invasion. Finally, the expression of VEGF-C was notably increased in HCC tissues and cell lines. These findings suggest that miR-101 exerts a suppressive effect on HCC cell migration and invasion, at least in part through the direct inhibition of VEGF-C protein expression. Therefore, the miR-101/VEGF-C axis may serve as a potential therapeutic target for HCC metastasis.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; invasion; microRNA-101; migration; vascular endothelial growth factor-C.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Methylation-mediated repression of microRNA-129-2 suppresses cell aggressiveness by inhibiting high mobility group box 1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 14;7(24):36909-36923. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9377. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27191994 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of invasion-metastasis-associated microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma based on bioinformatic analysis and experimental validation.J Transl Med. 2018 Sep 29;16(1):266. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1639-8. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30268144 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-125b suppresses the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif.Oncol Lett. 2015 Apr;9(4):1971-1975. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.2973. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Oncol Lett. 2015. PMID: 25789078 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-608 acts as a prognostic marker and inhibits the cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by macrophage migration inhibitory factor.Tumour Biol. 2016 Mar;37(3):3823-30. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4213-5. Epub 2015 Oct 16. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26474589
-
MicroRNA-188-5p suppresses tumor cell proliferation and metastasis by directly targeting FGF5 in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2015 Oct;63(4):874-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.05.008. Epub 2015 May 18. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25998163
Cited by
-
A narrative review of papillary thyroid carcinoma-related long non-coding RNAs and their relevance to malignant tumors.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 30;14(3):2125-2149. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1038. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40224997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apigenin sensitizes BEL-7402/ADM cells to doxorubicin through inhibiting miR-101/Nrf2 pathway.Oncotarget. 2017 May 30;8(47):82085-82091. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18294. eCollection 2017 Oct 10. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29137246 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of strand-specific miRNA-101-3p and miRNA-101-5p for hepatocellular carcinoma and a bioinformatic analysis of their possible mechanism of action.FEBS Open Bio. 2017 Dec 20;8(1):64-84. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12349. eCollection 2018 Jan. FEBS Open Bio. 2017. PMID: 29321958 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes VEGF-C-dependent lymphangiogenesis by suppressing miR-624-3p in human chondrosarcoma cells.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Aug 3;8(8):e2964. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.354. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28771226 Free PMC article.
-
Solamargine inhibits the migration and invasion of HepG2 cells by blocking epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.Oncol Lett. 2017 Jul;14(1):447-452. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6147. Epub 2017 May 10. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28693190 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
