Hepatocyte growth factor increases the invasive potential of PC-3 human prostate cancer cells via an ERK/MAPK and Zeb-1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 26870279
- PMCID: PMC4727112
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2015.3943
Hepatocyte growth factor increases the invasive potential of PC-3 human prostate cancer cells via an ERK/MAPK and Zeb-1 signaling pathway
Abstract
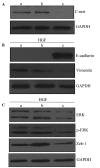
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) has been implicated in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in numerous types of cancer. However, to the best of our knowledge, there has been no previous evidence that HGF has a role in prostate cancer. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of HGF on EMT and invasive potential, as well as the underlying molecular mechanisms, in a human prostate cancer cell line. Therefore, PC-3 cells were treated with various concentrations of HGF for varying durations. EMT-associated proteins, including E-cadherin and vimentin, were examined by western blot analysis. The effects of HGF on cell proliferation, migration, invasion and tumorigenicity were assessed using MTT, wound-healing, Transwell and soft-agar assays. Subsequently, the role of c-Met in the mediation of EMT-like changes was investigated using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, western blot analysis and gene knockdown by small interfering RNA. Finally, western blot analysis was used to quantify the expression of a downstream transcription factor and extracellular signal-related kinase/mitogen activated protein kinase (ERK/MAPK) signaling pathway proteins. The results indicated that treatment with HGF induced EMT-like changes and enhanced the invasive potential of PC-3 cells. There was an increase in the expression of ERK, phosphorylated-ERK and zinc finger E-box binding homeobox-1 (Zeb-1), suggesting that EMT-like changes may be mediated through the ERK/MAPK and Zeb-1 signaling pathway. Furthermore, HGF-mediated EMT-like changes were associated with c-Met activation, and these changes were able to be blocked by c-Met knockdown. The present study demonstrated that HGF-induced EMT increased the invasive potential of PC-3 human prostate cancer cells through activating the ERK/MAPK and Zeb-1 signaling pathway.
Keywords: epithelial-mesenchymal transition; extracellular signal-related kinase/mitogen activated protein kinase signaling pathway; hepatocyte growth factor; prostate cancer; zinc finger E-box binding homeobox.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and Akt activation play a critical role in the process of hepatocyte growth factor-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Int J Oncol. 2013 Feb;42(2):556-64. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1726. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23229794
-
Curcumin mediates reversion of HGF-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via inhibition of c-Met expression in DU145 cells.Oncol Lett. 2016 Feb;11(2):1499-1505. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.4063. Epub 2015 Dec 28. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 26893768 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of c-Met increases the tumor invasion of human prostate LNCaP cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.Oncol Lett. 2014 Oct;8(4):1618-1624. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.2390. Epub 2014 Jul 28. Oncol Lett. 2014. PMID: 25202379 Free PMC article.
-
Role of HGF/MET axis in resistance of lung cancer to contemporary management.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2012 Sep;1(3):179-93. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2012.09.04. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 25806180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pancreatic Cancer Treatment Targeting the HGF/c-MET Pathway: The MEK Inhibitor Trametinib.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Mar 5;16(5):1056. doi: 10.3390/cancers16051056. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473413 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of AKR1C3 significantly enhances human prostate cancer cells resistance to radiation.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):48050-48058. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10347. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27385003 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Matrix Influencing HGF/c-MET Signaling Pathway: Impact on Cancer Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 24;19(11):3300. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113300. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30352967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostate-specific markers to identify rare prostate cancer cells in liquid biopsies.Nat Rev Urol. 2019 Jan;16(1):7-22. doi: 10.1038/s41585-018-0119-5. Nat Rev Urol. 2019. PMID: 30479377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of ZEB1 Function and Molecular Associations in Tumor Progression and Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 7;14(8):1864. doi: 10.3390/cancers14081864. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35454770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol Suppresses Prostate Cancer Epithelial Cell Scatter/Invasion by Targeting Inhibition of Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF) Secretion by Prostate Stromal Cells and Upregulation of E-cadherin by Prostate Cancer Epithelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 4;21(5):1760. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051760. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32143478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shah RB, Mehra R, Chinnaiyan AM, Shen R, Ghosh D, Zhou M, Macvicar GR, Varambally S, Harwood J, Bismar TA, et al. Androgen-independent prostate cancer is a heterogeneous group of diseases: Lessons from a rapid autopsy program. Cancer Res. 2004;64:9209–9216. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2442. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
