The Cytoplasmic and Periplasmic Expression Levels and Folding of Organophosphorus Hydrolase Enzyme in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 26870308
- PMCID: PMC4746795
- DOI: 10.5812/jjm.17790
The Cytoplasmic and Periplasmic Expression Levels and Folding of Organophosphorus Hydrolase Enzyme in Escherichia coli
Abstract
Background: Organophosphorus hydrolase (OPH) is a type of organophosphate-degrading enzyme which is widely used in the bioremediation process.
Objectives: In this study, the periplasmic and cytoplasmic productions and the activity of recombinant OPH in Escherichia coli were investigated and compared using two pET systems (pET21a and pET26b).
Materials and methods: The sequence encoding the opd gene was synthesized and expressed in the form of inclusion body using pET21a-opd and in the periplasmic space in pET26b-opd.
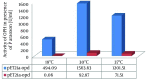
Results: Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) analysis showed a band of about 37 kDa with a maximum expression level at 30°C from pET21a-opd.However, the obtained results of the periplasmic space extraction of OPH (pET26b-opd) showed a very weak band, while the cytoplasmic expression of OPH (pET21a-opd) produced a strong protein band.
Conclusions: The activities studied by the production of PNP were determined by following the increase at 410 nm. The maximum PNP was produced at 30°C with an optical density of 10.62 in the presence of cytoplasmic expression of OPH (pET21a-opd). Consequently, our results suggest cytoplasmic expression system as an appropriate candidate with a high amount of OPH in spite of inclusion body formation, which needs an additional refolding step.
Keywords: Cytoplasmic; Escherichia coli; Organophosphorus; Periplasmic.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Coexpression of molecular chaperone enhances activity and export of organophosphorus hydrolase in Escherichia coli.Biotechnol Prog. 2012 Jul;28(4):925-30. doi: 10.1002/btpr.1556. Epub 2012 Jun 8. Biotechnol Prog. 2012. PMID: 22581577
-
Versatile signal peptide of Flavobacterium-originated organophosphorus hydrolase for efficient periplasmic translocation of heterologous proteins in Escherichia coli.Biotechnol Prog. 2016 Jul 8;32(4):848-54. doi: 10.1002/btpr.2274. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Biotechnol Prog. 2016. PMID: 27071499
-
Comparison of the cytoplasmic and periplasmic production of reteplase in Escherichia coli.Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2013;43(7):613-23. doi: 10.1080/10826068.2013.764896. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23768109
-
Advances in detection of hazardous organophosphorus compounds using organophosphorus hydrolase based biosensors.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2019 May;49(5):387-410. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2019.1626800. Epub 2019 Jul 3. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31268806 Review.
-
Rational design of organophosphorus hydrolase for altered substrate specificities.Chem Biol Interact. 1999 May 14;119-120:211-23. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(99)00030-7. Chem Biol Interact. 1999. PMID: 10421455 Review.
Cited by
-
Effective refolding of a cysteine rich glycoside hydrolase family 19 recombinant chitinase from Streptomyces griseus by reverse dilution and affinity chromatography.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 22;15(10):e0241074. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241074. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33091044 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of Supercharging as A Strategy to Enhance the Solubility and Plasminogen Cleavage Activity of Reteplase.Iran J Biotechnol. 2020 Oct 1;18(4):e2556. doi: 10.30498/IJB.2020.2556. eCollection 2020 Oct. Iran J Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 34056023 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant and Chimeric Disintegrins in Preclinical Research.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Aug 7;10(8):321. doi: 10.3390/toxins10080321. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30087285 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bardin PG, van Eeden SF, Moolman JA, Foden AP, Joubert JR. Organophosphate and carbamate poisoning. Arch Intern Med. 1994;154(13):1433–41. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
