Comparison of the effects of melatonin and genistein on radiation-induced nephrotoxicity: Results of an experimental study
- PMID: 26870332
- PMCID: PMC4726846
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2015.547
Comparison of the effects of melatonin and genistein on radiation-induced nephrotoxicity: Results of an experimental study
Abstract
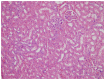
The aim of the present study was to compare the effects of melatonin and genistein on radiation-induced nephrotoxicity (RIN). A total of 70 Swiss Albino mice were divided into 7 groups. Five control groups were defined, which were sham irradiation (C, G1), radiation therapy only (RT, G2), melatonin (M, G3), genistein (G, G4) and polyethylene glycol-400 (G5), respectively. The co-treatment groups were the RT plus melatonin (RT+M, G6) and RT plus genistein (RT+G, G7) groups. Irradiation was applied using a cobalt-60 teletherapy machine (80-cm fixed source-to-surface distance, 2.5-cm depth). Melatonin was administered (100 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection) 30 min before the single dose of irradiation, whereas genistein was administered (200 mg/kg, subcutaneous injection) 1 day before the single dose of irradiation. All the mice were sacrificed 6 months after irradiation. As an end point, the extent of renal tubular atrophy for each mouse was quantified with image analysis of histological sections of the kidney. Tissue malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were also measured in each animal. In the histopathological examination of the mouse kidneys, there was a statistically significant reduction (P<0.05) in the presence of tubular atrophy between the RT+M and RT+G groups and the RT group. There was a statistically significant increase in MDA levels in the irradiated versus sham groups (RT vs. C; P<0.05); however, MDA levels were significantly decreased by co-treatment with melatonin or genistein vs. RT alone (RT+M and RT+G vs. RT; P<0.05). In conclusion, the present experimental study showed that melatonin and genistein supplementation prior to irradiation-protected mice against RIN, which may have therapeutic implications for radiation-induced injuries.
Keywords: genistein; melatonin; mice; nephrotoxicity; radiation; radioprotection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effects of genistein and melatonin on mouse liver injury induced by whole-body ionising radiation.Mol Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb;10(2):261-266. doi: 10.3892/mco.2018.1790. Epub 2018 Dec 11. Mol Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30680205 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Radioprotective Effects of Melatonin Against Ionizing Radiation-Induced Muscle Tissue Injury.Curr Radiopharm. 2019;12(3):247-255. doi: 10.2174/1874471012666190219120329. Curr Radiopharm. 2019. PMID: 30806333
-
Radioprotective effects of melatonin on radiation-induced cataract.J Radiat Res. 2005 Jun;46(2):277-82. doi: 10.1269/jrr.46.277. J Radiat Res. 2005. PMID: 15988147
-
Melatonin's protective effect on the salivary gland against ionized radiation damage in rats.J Oral Pathol Med. 2016 Jul;45(6):444-9. doi: 10.1111/jop.12386. Epub 2016 Jan 12. J Oral Pathol Med. 2016. PMID: 26757153
-
Comparison of the protective roles of L-carnitine and amifostine against radiation-induced acute ovarian damage by histopathological and biochemical methods.J Cancer Res Ther. 2015 Apr-Jun;11(2):447-53. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.146091. J Cancer Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26148616
Cited by
-
Effects of Genistein on Common Kidney Diseases.Nutrients. 2022 Sep 13;14(18):3768. doi: 10.3390/nu14183768. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36145144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kidney cell DNA damage caused by combined exposure to volatile anaesthetics and 1 Gy or 2 Gy radiotherapy dose in vivo.Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2022 Apr 7;73(1):62-70. doi: 10.2478/aiht-2022-73-3600. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2022. PMID: 35390237 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Guardians: Natural Compounds as Radioprotectors in Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 25;25(13):6937. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136937. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism and therapeutic window of a genistein nanosuspension to protect against hematopoietic-acute radiation syndrome.J Radiat Res. 2019 May 1;60(3):308-317. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrz014. J Radiat Res. 2019. PMID: 31038675 Free PMC article.
-
The Genistein Supply and Elemental Composition of Rat Kidneys in an Induced Breast Cancer Model.Nutrients. 2025 Mar 28;17(7):1184. doi: 10.3390/nu17071184. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40218942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Robbins ME, Bonsib SM. Radiation nephropathy: A review. Scanning Microsc. 1995;9:535–560. - PubMed
-
- Bolling T, Schuck A, Rube C, Hesselmann S, Pape H, Dieckmann K, Pollinger B, Kortmann RD, Speiser-Held I, Meyer FM, et al. Therapy-associated late effects after irradiation of malignant diseases in childhood and adolescence. Feasibility analyses of a prospective multicenter register study. Strahlenther Onkol. 2006;182:443–449. (In German) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous