Effect of Coleus forskohlii and its major constituents on cytochrome P450 induction
- PMID: 26870691
- PMCID: PMC4737967
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2014.11.027
Effect of Coleus forskohlii and its major constituents on cytochrome P450 induction
Abstract
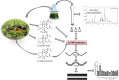
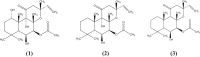
Coleus forskohlii Briq. has been used traditionally for the treatment of several ailments since antiquity in Ayurveda. In the present study, an approach has been made to evaluate the effect of C. forskohlii and its major constituents on cytochrome P450 (CYP3A, CYP2B, and CYP2C) mRNA expression in rat hepatocytes. To gain better understanding of the herb-drug interaction potential of the chemical constituents present in C. forskohlii, the extract was subjected to column chromatography followed by standardization with respect to forskolin, 1-deoxyforskolin, and 1,9-dideoxyforskolin using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC). Hepatocytes were treated with extracts, fractions, and phytoconstituents, followed by extraction and purification of total mRNA. Study of mRNA expression was carried out through reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, followed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Results revealed that the test substances did not show any significant mRNA expression compared to the control against CYP3A, CYP2B, and CYP2C. Positive controls such as dexamethasone and rifampin showed significantly high (p < 0.001) induction potential compared to the control. It can be concluded that C. forskohlii and its major constituents may not be involved in CYP450 induction-based drug interaction.
Keywords: Coleus forskohlii; Cytochrome P450; Drug interaction; Standardization; mRNA expression.
Figures

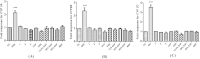
Similar articles
-
Coleus forskohlii extract attenuates the hypoglycemic effect of tolbutamide in vivo via a hepatic cytochrome P450-mediated mechanism.Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2014;55(2):73-8. doi: 10.3358/shokueishi.55.73. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2014. PMID: 24990552
-
Coleus forskohlii extract induces hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes in mice.Food Chem Toxicol. 2012 Mar;50(3-4):750-5. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2011.11.054. Epub 2011 Dec 8. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22178802
-
Quantitative analysis of forskolin in Coleus forskohlii (Lamiaceae) by reversed-phase liquid chromatography.J AOAC Int. 2003 May-Jun;86(3):467-70. J AOAC Int. 2003. PMID: 12852560
-
Hepatic cytochrome P450 mediates interaction between warfarin and Coleus forskohlii extract in vivo and in vitro.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2012 Dec;64(12):1793-801. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.2012.01563.x. Epub 2012 Jul 19. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23146043
-
Anti-HIV diterpenes from Coleus forskohlii.Nat Prod Commun. 2009 Sep;4(9):1173-5. Nat Prod Commun. 2009. PMID: 19831022
Cited by
-
In Vitro Assessment of the Interaction Potential of Ocimum basilicum (L.) Extracts on CYP2B6, 3A4, and Rifampicin Metabolism.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Apr 30;11:517. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00517. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32425779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alasbahi R.H., Melzig M.F. Plectranthus barbatus: a review of phytochemistry, ethnobotanical uses and pharmacology—part 2. Planta Med. 2010;76:753–765. - PubMed
-
- Murugesan S., Rajeshkannan C., Sumathi R., Manivachakam P., Suresh Babu D. Bioactivity of root hexane extract of Coleus forskohlii Briq. Labiatae: GC/MS/MS characterization and identification. Eur J Exp Biol. 2012;2:1469–1473.
-
- Foster S., Johnson R. 1st ed. National Geographic Society; Washington: 2006. Desk Reference to Nature's Medicine.
-
- Virgona N., Yokotani K., Yamazaki Y. Coleus forskohlii extract induces hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012;50:750–755. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
