Cyclic AMP Response Element Binding Protein Mediates Pathological Retinal Neovascularization via Modulating DLL4-NOTCH1 Signaling
- PMID: 26870802
- PMCID: PMC4740322
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.09.042
Cyclic AMP Response Element Binding Protein Mediates Pathological Retinal Neovascularization via Modulating DLL4-NOTCH1 Signaling
Abstract
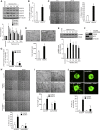
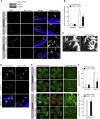
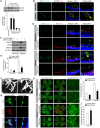
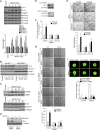
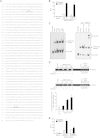
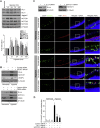
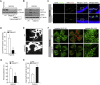
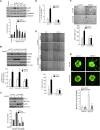
Retinal neovascularization is the most common cause of moderate to severe vision loss in all age groups. Despite the use of anti-VEGFA therapies, this complication continues to cause blindness, suggesting a role for additional molecules in retinal neovascularization. Besides VEGFA and VEGFB, hypoxia induced VEGFC expression robustly. Based on this finding, we tested the role of VEGFC in pathological retinal angiogenesis. VEGFC induced proliferation, migration, sprouting and tube formation of human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (HRMVECs) and these responses require CREB-mediated DLL4 expression and NOTCH1 activation. Furthermore, down regulation of VEGFC levels substantially reduced tip cell formation and retinal neovascularization in vivo. In addition, we observed that CREB via modulating the DLL4-NOTCH1 signaling mediates VEGFC-induced tip cell formation and retinal neovascularization. In regard to upstream mechanism, we found that down regulation of p38β levels inhibited hypoxia-induced CREB-DLL4-NOTCH1 activation, tip cell formation, sprouting and retinal neovascularization. Based on these findings, it may be suggested that VEGFC besides its role in the regulation of lymphangiogenesis also plays a role in pathological retinal angiogenesis and this effect depends on p38β and CREB-mediated activation of DLL4-NOTCH1 signaling.
Keywords: CREB; DLL4; NOTCH1; Retinal neovascularization; VEGFC.
Figures

Comment in
-
Emerging Role of VEGFC in Pathological Angiogenesis.EBioMedicine. 2015 Nov 10;2(11):1588-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.11.006. eCollection 2015 Nov. EBioMedicine. 2015. PMID: 26870778 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
PKCθ-JunB axis via upregulation of VEGFR3 expression mediates hypoxia-induced pathological retinal neovascularization.Cell Death Dis. 2020 May 7;11(5):325. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2522-0. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32382040 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted siRNA Delivery Against RUNX1 Via tFNA: Inhibiting Retinal Neovascularization and Restoring Vessels Through Dll4/Notch1 Signaling.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Mar 3;66(3):39. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.3.39. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40105819 Free PMC article.
-
The Notch1-Dll4 signaling pathway regulates mouse postnatal lymphatic development.Blood. 2011 Aug 18;118(7):1989-97. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-11-319129. Epub 2011 Jun 23. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21700774
-
Common cues regulate neural and vascular patterning.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007 Aug;17(4):332-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2007.07.004. Epub 2007 Aug 9. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007. PMID: 17692512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Recent Advances in the Function and Mechanism of Caveolin-1 in Retinal Neovascularization.Curr Drug Targets. 2024;25(7):465-472. doi: 10.2174/0113894501310201240403065930. Curr Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38591209 Review.
Cited by
-
CRISPR Technology for Ocular Angiogenesis.Front Genome Ed. 2020 Dec 22;2:594984. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2020.594984. eCollection 2020. Front Genome Ed. 2020. PMID: 34713223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paxillin promotes the migration and angiogenesis of HUVECs and affects angiogenesis in the mouse cornea.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Aug;20(2):901-909. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8751. Epub 2020 May 14. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32742332 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Valproic Acid and Mitomycin C Combination Therapy in a Rabbit Model of Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022 Jan 3;11(1):30. doi: 10.1167/tvst.11.1.30. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35044442 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Herbal Eye Drops Exhibit Neuroprotective and Intraocular Pressure-Reducing Effects in a Glaucoma Rat Model.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 May 1;14(5):549. doi: 10.3390/antiox14050549. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427431 Free PMC article.
-
Thromboxane prostanoid signaling in macrophages attenuates lymphedema and facilitates lymphangiogenesis in mice : TP signaling and lymphangiogenesis.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Oct;50(10):7981-7993. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08620-0. Epub 2023 Aug 4. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37540456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramovitch R., Tavor E., Jacob-Hirsch J., Zeira E., Amariglio N., Pappo O., Rechavi G., Galun E., Honigman A. A pivotal role of cyclic amp-responsive element binding protein in tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1338–1346. - PubMed
-
- Aiello L.P., Avery R.L., Arrigg P.G., Keyt B.A., Jampel H.D., Shah S.T., Pasquale L.R., Thieme H., Iwamoto M.A., Park J.E., Nguyen H.V., Aiello L.M., Ferrara N., King G.L. Vascular endothelial growth factor in ocular fluid of patients with diabetic retinopathy and other retinal disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994;331:1480–1487. - PubMed
-
- Alon T., Hemo I., Itin A., Pe'er J., Stone J., Keshet E. Vascular endothelial growth factor acts as a survival factor for newly formed retinal vessels and has implications for retinopathy of prematurity. Nat. Med. 1995;1:1024–1028. - PubMed
-
- Andreoli C.M., Miller J.W. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy for ocular neovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2007;18:502–508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

