Cyclic AMP Response Element Binding Protein Mediates Pathological Retinal Neovascularization via Modulating DLL4-NOTCH1 Signaling
- PMID: 26870802
- PMCID: PMC4740322
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.09.042
Cyclic AMP Response Element Binding Protein Mediates Pathological Retinal Neovascularization via Modulating DLL4-NOTCH1 Signaling
Abstract
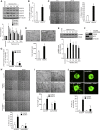
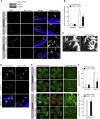
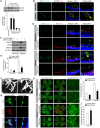
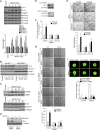
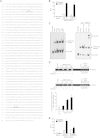
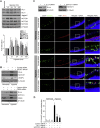
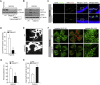
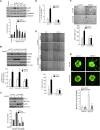
Retinal neovascularization is the most common cause of moderate to severe vision loss in all age groups. Despite the use of anti-VEGFA therapies, this complication continues to cause blindness, suggesting a role for additional molecules in retinal neovascularization. Besides VEGFA and VEGFB, hypoxia induced VEGFC expression robustly. Based on this finding, we tested the role of VEGFC in pathological retinal angiogenesis. VEGFC induced proliferation, migration, sprouting and tube formation of human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (HRMVECs) and these responses require CREB-mediated DLL4 expression and NOTCH1 activation. Furthermore, down regulation of VEGFC levels substantially reduced tip cell formation and retinal neovascularization in vivo. In addition, we observed that CREB via modulating the DLL4-NOTCH1 signaling mediates VEGFC-induced tip cell formation and retinal neovascularization. In regard to upstream mechanism, we found that down regulation of p38β levels inhibited hypoxia-induced CREB-DLL4-NOTCH1 activation, tip cell formation, sprouting and retinal neovascularization. Based on these findings, it may be suggested that VEGFC besides its role in the regulation of lymphangiogenesis also plays a role in pathological retinal angiogenesis and this effect depends on p38β and CREB-mediated activation of DLL4-NOTCH1 signaling.
Keywords: CREB; DLL4; NOTCH1; Retinal neovascularization; VEGFC.
Figures

Comment in
-
Emerging Role of VEGFC in Pathological Angiogenesis.EBioMedicine. 2015 Nov 10;2(11):1588-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.11.006. eCollection 2015 Nov. EBioMedicine. 2015. PMID: 26870778 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Abramovitch R., Tavor E., Jacob-Hirsch J., Zeira E., Amariglio N., Pappo O., Rechavi G., Galun E., Honigman A. A pivotal role of cyclic amp-responsive element binding protein in tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1338–1346. - PubMed
-
- Aiello L.P., Avery R.L., Arrigg P.G., Keyt B.A., Jampel H.D., Shah S.T., Pasquale L.R., Thieme H., Iwamoto M.A., Park J.E., Nguyen H.V., Aiello L.M., Ferrara N., King G.L. Vascular endothelial growth factor in ocular fluid of patients with diabetic retinopathy and other retinal disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994;331:1480–1487. - PubMed
-
- Alon T., Hemo I., Itin A., Pe'er J., Stone J., Keshet E. Vascular endothelial growth factor acts as a survival factor for newly formed retinal vessels and has implications for retinopathy of prematurity. Nat. Med. 1995;1:1024–1028. - PubMed
-
- Andreoli C.M., Miller J.W. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy for ocular neovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2007;18:502–508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

