Stress Granules Modulate SYK to Cause Microglial Cell Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 26870803
- PMCID: PMC4740304
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.09.053
Stress Granules Modulate SYK to Cause Microglial Cell Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Syk and ye shall find" [EBioMedicine 2 (11) (2015) 190-1591].EBioMedicine. 2016 Jun;8:349. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.05.033. Epub 2016 May 29. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27428444 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
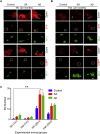
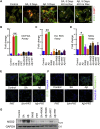
Microglial cells in the brains of Alzheimer's patients are known to be recruited to amyloid-beta (Aβ) plaques where they exhibit an activated phenotype, but are defective for plaque removal by phagocytosis. In this study, we show that microglia stressed by exposure to sodium arsenite or Aβ(1-42) peptides or fibrils form extensive stress granules (SGs) to which the tyrosine kinase, SYK, is recruited. SYK enhances the formation of SGs, is active within the resulting SGs and stimulates the production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species that are toxic to neuronal cells. This sequestration of SYK inhibits the ability of microglial cells to phagocytose Escherichia coli or Aβ fibrils. We find that aged microglial cells are more susceptible to the formation of SGs; and SGs containing SYK and phosphotyrosine are prevalent in the brains of patients with severe Alzheimer's disease. Phagocytic activity can be restored to stressed microglial cells by treatment with IgG, suggesting a mechanism to explain the therapeutic efficacy of intravenous IgG. These studies describe a mechanism by which stress, including exposure to Aβ, compromises the function of microglial cells in Alzheimer's disease and suggest approaches to restore activity to dysfunctional microglial cells.
Keywords: AD, Alzheimer's disease; Alzheimer's disease; Amyloid-beta; Aβ, amyloid-beta; IgG, immunoglobulin G; MG, microglial cells; Microglial cells; Neurodegenerative disease; SYK tyrosine kinase; Stress granules.
Figures








Comment in
-
Syk and Yea Shall Find.EBioMedicine. 2015 Nov 10;2(11):1590-1. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.11.012. eCollection 2015 Nov. EBioMedicine. 2015. PMID: 26870779 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Anderson P., Kedersha N. Stress granules: the Tao of RNA triage. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008;33:141–150. - PubMed
-
- Angata T., Kerr S.C., Greaves D.R., Varki N.M., Crocker P.R., Varki A. Cloning and characterization of human siglec-11: a recently evolved signaling molecule that can interact with SHP-1 and SHP-2 and is expressed by tissue macrophages, including brain microglia. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:24466–24474. - PubMed
-
- Barcia C., Ross C.M., Annese V., Gómez A., Ros-Bernal F., Aguado-Llera D., Martinez-Pagán E., de Pablos V., Fernandez-Villalba E., Herrero M.T. IFN-γ signaling, with the synergistic contribution of TNF-α, mediates cell specific microglial and astroglial activation in experimental models of Parkinson's disease. Cell Death Dis. 2012;3 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

