Small CD4 Mimetics Prevent HIV-1 Uninfected Bystander CD4 + T Cell Killing Mediated by Antibody-dependent Cell-mediated Cytotoxicity
- PMID: 26870823
- PMCID: PMC4739418
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.12.004
Small CD4 Mimetics Prevent HIV-1 Uninfected Bystander CD4 + T Cell Killing Mediated by Antibody-dependent Cell-mediated Cytotoxicity
Abstract
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection causes a progressive depletion of CD4 + T cells. Despite its importance for HIV-1 pathogenesis, the precise mechanisms underlying CD4 + T-cell depletion remain incompletely understood. Here we make the surprising observation that antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) mediates the death of uninfected bystander CD4 + T cells in cultures of HIV-1-infected cells. While HIV-1-infected cells are protected from ADCC by the action of the viral Vpu and Nef proteins, uninfected bystander CD4 + T cells bind gp120 shed from productively infected cells and are efficiently recognized by ADCC-mediating antibodies. Thus, gp120 shedding represents a viral mechanism to divert ADCC responses towards uninfected bystander CD4 + T cells. Importantly, CD4-mimetic molecules redirect ADCC responses from uninfected bystander cells to HIV-1-infected cells; therefore, CD4-mimetic compounds might have therapeutic utility in new strategies aimed at specifically eliminating HIV-1-infected cells.
Keywords: ADCC; Bystander killing; CD4; CD4-bound conformation; CD4-mimetics; Envelope glycoproteins; HIV-1; Non-neutralizing antibodies; gp120.
Figures
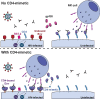
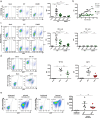
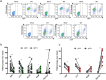
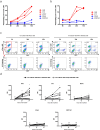
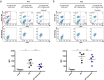
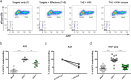
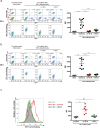
Comment in
-
The Yin and Yang of ADCC-Mediating Antibodies.EBioMedicine. 2016 Jan 8;3:10-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.01.003. eCollection 2016 Jan. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 26870833 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Uninfected Bystander Cells Impact the Measurement of HIV-Specific Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Responses.mBio. 2018 Mar 20;9(2):e00358-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00358-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29559570 Free PMC article.
-
Co-receptor Binding Site Antibodies Enable CD4-Mimetics to Expose Conserved Anti-cluster A ADCC Epitopes on HIV-1 Envelope Glycoproteins.EBioMedicine. 2016 Oct;12:208-218. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.09.004. Epub 2016 Sep 9. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27633463 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity-Competent Antibodies against HIV-1-Infected Cells in Plasma from HIV-Infected Subjects.mBio. 2019 Dec 17;10(6):e02690-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02690-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31848282 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking HIV-1 Env: implications for antibody attack.AIDS Res Ther. 2017 Sep 12;14(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12981-017-0168-5. AIDS Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28893275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of HIV-1 Envelope Conformation on ADCC Responses.Trends Microbiol. 2018 Apr;26(4):253-265. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.10.007. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Trends Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29162391 Review.
Cited by
-
CD4- and Time-Dependent Susceptibility of HIV-1-Infected Cells to Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity.J Virol. 2019 May 1;93(10):e01901-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01901-18. Print 2019 May 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30842324 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 gp120 envelope glycoprotein determinants for cytokine burst in human monocytes.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 27;12(3):e0174550. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174550. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28346521 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Ability of Plant-Derived PGT121 Glycovariants To Eliminate HIV-1-Infected Cells.J Virol. 2021 Aug 25;95(18):e0079621. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00796-21. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34232070 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity targeting CD4-inducible epitopes predicts mortality in HIV-infected infants.EBioMedicine. 2019 Sep;47:257-268. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.08.072. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31501077 Free PMC article.
-
The Conformational States of the HIV-1 Envelope Glycoproteins.Trends Microbiol. 2020 Aug;28(8):655-667. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.03.007. Epub 2020 May 14. Trends Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32418859 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alimonti J.B., Ball T.B., Fowke K.R. Mechanisms of CD4 + T lymphocyte cell death in human immunodeficiency virus infection and AIDS. J. Gen. Virol. 2003;84:1649–1661. - PubMed
-
- Alkhatib G., Combadiere C., Broder C.C., Feng Y., Kennedy P.E., Murphy P.M., Berger E.A. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science. 1996;272:1955–1958. - PubMed
-
- Allan J.S., Coligan J.E., Barin F., Mclane M.F., Sodroski J.G., Rosen C.A., Haseltine W.A., Lee T.H., Essex M. Major glycoprotein antigens that induce antibodies in AIDS patients are encoded by HTLV-III. Science. 1985;228:1091–1094. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

