RHAMM splice variants confer radiosensitivity in human breast cancer cell lines
- PMID: 26870892
- PMCID: PMC5008296
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7258
RHAMM splice variants confer radiosensitivity in human breast cancer cell lines
Abstract
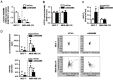
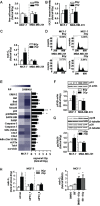
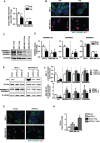
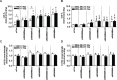
Biomarkers for prognosis in radiotherapy-treated breast cancer patients are urgently needed and important to stratify patients for adjuvant therapies. Recently, a role of the receptor of hyaluronan-mediated motility (RHAMM) has been suggested for tumor progression. Our aim was (i) to investigate the prognostic value of RHAMM in breast cancer and (ii) to unravel its potential function in the radiosusceptibility of breast cancer cells. We demonstrate that RHAMM mRNA expression in breast cancer biopsies is inversely correlated with tumor grade and overall survival. Radiosusceptibility in vitro was evaluated by sub-G1 analysis (apoptosis) and determination of the proliferation rate. The potential role of RHAMM was addressed by short interfering RNAs against RHAMM and its splice variants. High expression of RHAMMv1/v2 in p53 wild type cells (MCF-7) induced cellular apoptosis in response to ionizing radiation. In comparison, in p53 mutated cells (MDA-MB-231) RHAMMv1/v2 was expressed sparsely resulting in resistance towards irradiation induced apoptosis. Proliferation capacity was not altered by ionizing radiation in both cell lines. Importantly, pharmacological inhibition of the major ligand of RHAMM, hyaluronan, sensitized both cell lines towards radiation induced cell death. Based on the present data, we conclude that the detection of RHAMM splice variants in correlation with the p53 mutation status could help to predict the susceptibility of breast cancer cells to radiotherapy. Additionally, our studies raise the possibility that the response to radiotherapy in selected cohorts may be improved by pharmaceutical strategies against RHAMM and its ligand hyaluronan.
Keywords: RHAMM; breast cancer; cell death; extracellular matrix; ionizing radiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Favourable and unfavourable effects on long-term survival of radiotherapy for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2000;355:1757–1770. - PubMed
-
- Mokbel K. Current management of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003;8:18–22. - PubMed
-
- Boyages J, Delaney G, Taylor R. Predictors of local recurrence after treatment of ductal carcinoma in situ: a meta-analysis. Cancer. 1999;85:616–28. - PubMed
-
- Hooning MJ, Botma A, Aleman BM, Baaijens MH, Bartelink H, Klijn JG, Taylor CW, van Leeuwen FE. Long-term risk of cardiovascular disease in 10-year survivors of breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007;99:365–75. - PubMed
-
- Wilder RB, Curcio LD, Khanijou RK, Eisner ME, Kakkis JL, Chittenden L, Agustin J, Lizarde J, Mesa AV, Macedo JC, Ravera J, Tokita KM. Results with accelerated partial breast irradiation in terms of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and human growth factor receptor 2 status. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010;78:799–803. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

