Diallyl disulfide suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and proliferation by downregulation of LIMK1 in gastric cancer
- PMID: 26871290
- PMCID: PMC4891135
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7252
Diallyl disulfide suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and proliferation by downregulation of LIMK1 in gastric cancer
Abstract
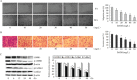
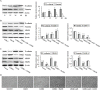
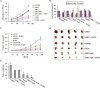
Diallyl disulfide (DADS) has been shown to have multi-targeted antitumor activities. We have previously discovered that it has a repressive effect on LIM kinase-1 (LIMK1) expression in gastric cancer MGC803 cells. This suggests that DADS may inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by downregulating LIMK1, resulting in the inhibition of invasion and growth in gastric cancer. In this study, we reveal that LIMK1 expression is correlated with tumor differentiation, invasion depth, clinical stage, lymph node metastasis, and poor prognosis. DADS downregulated the Rac1-Pak1/Rock1-LIMK1 pathway in MGC803 cells, as shown by decreased p-LIMK1 and p-cofilin1 levels, and suppressed cell migration and invasion. Knockdown and overexpression experiments performed in vitro demonstrated that downregulating LIMK1 with DADS resulted in restrained EMT that was coupled with decreased matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and increased tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 (TIMP-3) expression. In in vitro and in vivo experiments, the DADS-induced suppression of cell proliferation was enhanced and antagonized by the knockdown and overexpression of LIMK1, respectively. Similar results were observed for DADS-induced changes in the expression of vimentin, CD34, Ki-67, and E-cadherin in xenografted tumors. These results indicate that downregulation of LIMK1 by DADS could explain the inhibition of EMT, invasion and proliferation in gastric cancer cells.
Keywords: LIMK1; diallyl disulfide; gastric cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition; invasion; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Diallyl Disulfide: A Bioactive Garlic Compound with Anticancer Potential.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 22;13:943967. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.943967. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36071845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DADS downregulates the Rac1-ROCK1/PAK1-LIMK1-ADF/cofilin signaling pathway, inhibiting cell migration and invasion.Oncol Rep. 2013 Feb;29(2):605-12. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.2168. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23233092
-
Diallyl disulfide induces downregulation and inactivation of cofilin 1 differentiation via the Rac1/ROCK1/LIMK1 pathway in leukemia cells.Int J Oncol. 2020 Mar;56(3):772-782. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2020.4968. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Int J Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32124958 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential targets for diallyl disulfide in human gastric cancer MGC-803 cells using proteomics approaches.Oncol Rep. 2015 May;33(5):2484-94. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3859. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25812569
-
Suppression of angiogenesis and tumour progression by combretastatin and derivatives.Cancer Lett. 2017 Sep 10;403:289-295. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.06.032. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28688972 Review.
Cited by
-
PDZ and LIM Domain-Encoding Genes: Their Role in Cancer Development.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 19;15(20):5042. doi: 10.3390/cancers15205042. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RORα Suppresses Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Invasion in Human Gastric Cancer Cells via the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Front Oncol. 2019 Dec 6;9:1344. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01344. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. Retraction in: Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 28;10:607586. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.607586. PMID: 31867273 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Upregulation of miR-93 and inhibition of LIMK1 improve ventricular remodeling and alleviate cardiac dysfunction in rats with chronic heart failure by inhibiting RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway activation.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Sep 20;11(18):7570-7586. doi: 10.18632/aging.102272. Epub 2019 Sep 20. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31541994 Free PMC article.
-
The microRNAs miR-200b-3p and miR-429-5p target the LIMK1/CFL1 pathway to inhibit growth and motility of breast cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 12;8(49):85276-85289. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19205. eCollection 2017 Oct 17. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29156719 Free PMC article.
-
Diallyl Disulfide: A Bioactive Garlic Compound with Anticancer Potential.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 22;13:943967. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.943967. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36071845 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yi L, Su Q. Molecular mechanisms for the anti-cancer effects of diallyl disulfide. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;57:362–370. - PubMed
-
- Su B, Xiang SL, Su J, Tang HL, Liao QJ, Zhou YJ, Su Q. Diallyl disulfide increased histone acetylation and p21WAF1 expression in human gastric cancer cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochem & Pharmacol. 2012;1:1–10.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

