Integrated transcriptomic and proteomic analysis identifies protein kinase CK2 as a key signaling node in an inflammatory cytokine network in ovarian cancer cells
- PMID: 26871292
- PMCID: PMC4941267
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7255
Integrated transcriptomic and proteomic analysis identifies protein kinase CK2 as a key signaling node in an inflammatory cytokine network in ovarian cancer cells
Abstract
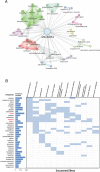
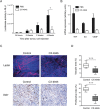
We previously showed how key pathways in cancer-related inflammation and Notch signaling are part of an autocrine malignant cell network in ovarian cancer. This network, which we named the "TNF network", has paracrine actions within the tumor microenvironment, influencing angiogenesis and the immune cell infiltrate.The aim of this study was to identify critical regulators in the signaling pathways of the TNF network in ovarian cancer cells that might be therapeutic targets. To achieve our aim, we used a systems biology approach, combining data from phospho-proteomic mass spectrometry and gene expression array analysis. Among the potential therapeutic kinase targets identified was the protein kinase Casein kinase II (CK2).Knockdown of CK2 expression in malignant cells by siRNA or treatment with the specific CK2 inhibitor CX-4945 significantly decreased Notch signaling and reduced constitutive cytokine release in ovarian cancer cell lines that expressed the TNF network as well as malignant cells isolated from high grade serous ovarian cancer ascites. The expression of the same cytokines was also inhibited after treatment with CX-4945 in a 3D organotypic model. CK2 inhibition was associated with concomitant inhibition of proliferative activity, reduced angiogenesis and experimental peritoneal ovarian tumor growth.In conclusion, we have identified kinases, particularly CK2, associated with the TNF network that may play a central role in sustaining the cytokine network and/or mediating its effects in ovarian cancer.
Keywords: inflammatory cytokine networks; microenvironment; ovarian cancer; systems biology; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
Figures



Similar articles
-
A dynamic inflammatory cytokine network in the human ovarian cancer microenvironment.Cancer Res. 2012 Jan 1;72(1):66-75. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2178. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22065722 Free PMC article.
-
The inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-alpha generates an autocrine tumor-promoting network in epithelial ovarian cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2007 Jan 15;67(2):585-92. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2941. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17234767 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental phosphoproteomics identifies the kinase CK2 as a driver of Hedgehog signaling and a therapeutic target in medulloblastoma.Sci Signal. 2018 Sep 11;11(547):eaau5147. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aau5147. Sci Signal. 2018. PMID: 30206138 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cancer progression by CK2: an emerging therapeutic target.Med Oncol. 2024 Mar 25;41(5):94. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02316-6. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38526625 Review.
-
Casein Kinase II (CK2), Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3) and Ikaros mediated regulation of leukemia.Adv Biol Regul. 2017 Aug;65:16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Adv Biol Regul. 2017. PMID: 28623166 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A meta-analysis and bioinformatics exploration of the diagnostic value and molecular mechanism of miR-193a-5p in lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2018 Oct;16(4):4114-4128. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9174. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30250529 Free PMC article.
-
CK2 in Cancer: Cellular and Biochemical Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Target.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2017 Jan 28;10(1):18. doi: 10.3390/ph10010018. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28134850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of the Adipokine Resistin in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 16;10(4):920. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040920. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35453670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TET1 reprograms the epithelial ovarian cancer epigenome and reveals casein kinase 2α as a therapeutic target.J Pathol. 2019 Jul;248(3):363-376. doi: 10.1002/path.5266. Epub 2019 Apr 23. J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30883733 Free PMC article.
-
Methodology of predicting novel key regulators in ovarian cancer network: a network theoretical approach.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 21;19(1):1129. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6309-6. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31752757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 2008;454:436–444. - PubMed
-
- Kulbe H, Chakravarty P, Leinster DA, Charles KA, Kwong J, Thompson RG, Coward JI, Schioppa T, Robinson SC, Gallagher WM, Galletta L, Australian Ovarian Cancer Study Group. Salako MA, Smyth JF, et al. A dynamic inflammatory cytokine network in the human ovarian cancer microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2012;72:66–75. - PMC - PubMed
-
- De Monte L, Reni M, Tassi E, Clavenna D, Papa I, Recalde H, Braga M, Di Carlo V, Doglioni C, Protti MP. Intratumor T helper type 2 cell infiltrate correlates with cancer-associated fibroblast thymic stromal lymphopoietin production and reduced survival in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Med. 2011;208:469–478. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

